Attachment Psychology Paper 1 Pdf Download
Today this article is looking at the attachment for paper 1 psychology a level with AQA and Attachment Psychology Paper 1 Pdf Download in 1 Click just go to the end of this article.
Caregiver infant interactions
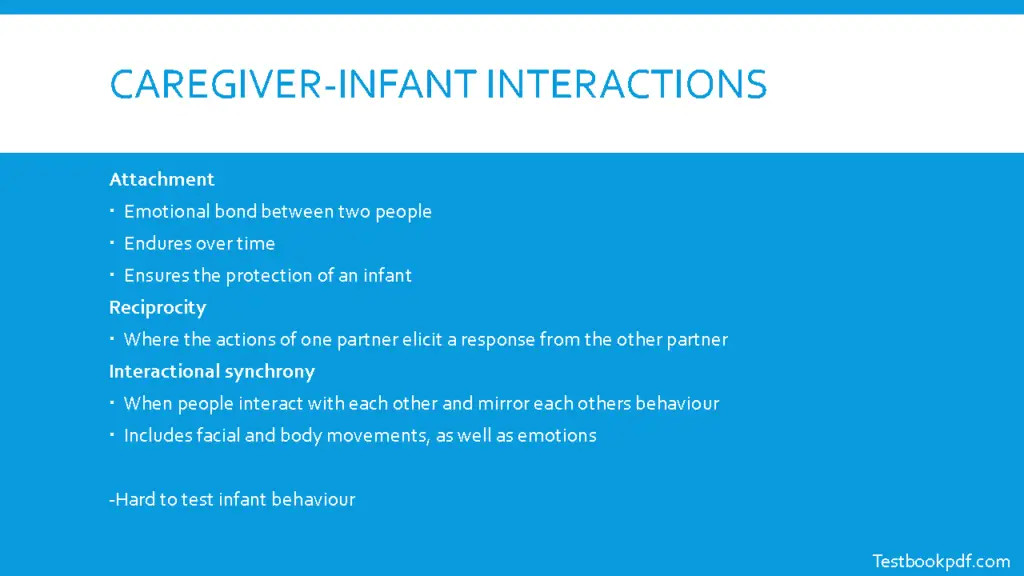
There are three main terms you need to know for the basis of this module so you’ve got attachment obviously which is the emotional bond between two people indoors over time and this relationship this attachment is Jules objection to an infant when looking at the mother’s information ship reciprocity and interactional synchrony are fairly similar ideas but wristlet reciprocity is where an action of one partner elicits a response from the other partner whereas interaction synchronous synchrony is when people interact with each other and marry each other behavior.
So both elicit a response to the other person but with reciprocity, it can be with anything with any sort of reaction, and whereas interaction secrets synchronous synchrony the response is exactly completely mirroring what the other individual is doing but obviously, it’s hard to test if their infant behavior because they aren’t aware of what they’re doing by the influence.
Interactional synchrony (Meltzoff and Moore)

So Meltzoff and Moore, the first thing we’ll be looking at is looking at interactional synchrony and so this was a controlled observation with 18 babies aged 12 to 27 days old and an actor did three different face stimuli which included the tongue protruding open mouth and pouty lips and one hand gesture as well the observations were recorded and watching the real-time slow-motion and frame by frame to ensure every slight different change of behavior was noticed and then these videos were judged by independent observers who did not know what the baby had seen.
So in terms of this, the people judging it the independent service actually know what behaved and what the activist doing and then each independent observer was asked to unite when they saw the mouth opening the termination of mouth opening tongue protrusion, and termination of temperature.
So for the stages of attachment you’ve got the first stage which is an indiscriminate attachment which is from birth to two months old where similar affection is shown to animate and inanimate objects but towards the end towards more than two months mark place this is when they start to prefer human interaction Stage two is the beginnings of attachment.
So two to six months old and that’s where they enjoy human company but can now tell the difference between familiar and unfamiliar faces however it is important to note here that even though they can recognize a difference there is no stranger anxiety still and then this stranger anxiety comes into play during the discriminate attachment stage 3 which is from several months onwards where stranger except for anxiety you begin to present themselves and for those of you that may not be aware stranger anxiety is the anxiety that creates when the infant is placed with someone they are not familiar with and then separation anxiety is the separation from their separation between the infant and their primary caregiver and then the fourth stage is multiple attachments which takes place eleventh from my eleventh class months on when this weather begins to form attachments with other people after forming an attachment with the primary attachment figure softly this includes like aunties uncles grandparents family friends etc obviously there is a slight cultural bias to this because obviously each Sasak culture treats baby babies in a different way and so see they’ll spell it differently and then well these a variation points are probably not in the right place there probably are more linked to the next slide which is actually the study that these stages of attachment are based on post.
Stages of attachment (Schaffer and Emerson)

The shape and Emerson study in which they looked at 660 children and mothers not lost so please know that spelling mistake I’m really sorry about that from working-class Glasgow in Scotland infant way aged five to twenty-three weeks old at the beginning of the study and were continued to be studying until their one-year-old they are visited every month and were recorded in seven everyday situations such as being left alone in a room and they obviously the intensity of the protest was recorded and who it was towards and from this, they form said it’s an attachment we just looked at with the findings but they also found really interesting a twenty percent of fathers were joint attachment figures and all the mother and by the age of one in three infants had over five secondary attachment.

so that was partly multiple attachments bit and obviously looking back at the previous slide this is where the cultural bias comes in because obviously it was just based in Glasgow Scotland not every baby is like babies from Scotland.
Animal studies

So looking at animal studies now it’s really really important to the attachment module so you’ve got Laurentiis study which involved a a like group of Gosling’s so half of the eggs were left with the mother Goose and then the other half of an incubator and then when they hatch they are the sort of wrens all their mother first the cool things that ended up imprinting on whatever they sought first is so consistently followed and Arends around if they were with him and then obviously if the eggs were still with the mother they would have consistently followed mother around and the definition imprinting is the innate readiness to develop a strong bond with a mother and then Lorenz thought like the critical period for which this imprinting imprinting has to take place we’ll see further hours of being home and if it found that without this it had long-term effects on the behavior of the Gosling’s such as struggling to mate with other geese in the future and then moving to a new study you’ve got the rhesus monkeys were placed into a cage individually with with both my mother and their cross mother and the food.
So we’re not they were given alternates between the Warran mother and then the time spent with each other was measured taking into consideration who had the food part of the study as well in mechanical bear was also placed into the cage to scare the monkey and even called their reactions and in every situation even when scared spent more time with the COFF mother which led to the idea of contact comfort and similar to the ghost things that had a lot of the impact of the input on the monkeys and found they’re less likely to mate as they got older and struggled in social situations and then obviously there’s confounding variables these studies are hard to generalize to humans because obviously we as humans will not react the same or behave the same as Gosling’s or rhesus monkeys and they’ll see because it had these lasting effects on the animals there are ethical issues involved.
Learning the theory of attachment

So looking at this learning theory of attachment is the classical conditioning operant conditioning and social learning theory.
So classical conditioning is a process of learning by association and was founded by Pavlov.
So in the top picture here you’ve got the dog and sort of shows that you’ve got the unconditioned stimulus which is the football full of food and then obviously the unconditioned response of a natural salivating process that an animal would make and then you have the neutral stimulus which was the whistle or the bell and offs that the dog would have no response to this but after conditioning the doctor to associate the bell with the food and created a conditioned response and therefore the Bell became the conditioned stimulus in terms of operant conditioning this is the process of learning through consequences which involve positive reinforcement negative reinforcement and punishment and studied was studied by Skinner and looking down to the second picture on the right-hand side with the rats.
So if the, if the behavior was if a good behavior was done then the rat, would be rewarded but if they did something wrong then they would be punished and then obviously social learning theory describes the children observing their parent’s behavior and imitating it and I think this sort of goes onto one of the bandura’s studies where he got children to watch this watch a video of a man being violent with a bobo doll and then they went they went to a play area where there wasn’t Popo down found that those who had watched the violent video were more like to be violent towards Vamo don’t rather than those who have not watched it but obviously the classical opera conditioning is based on animal studies.
So again similar to the Lorenz and Harlow studies it’s not the most reliable when it comes to generalizing humans.
Bowlby’s monotropic attachment theory

So Bowlby’s are really important when it comes to attachment he came up with a lot of great ideas.
So first the mono copy is the relationship an infant has with his or her primary attachment figure and as and is of special significance in the emotional development and both are used in Lorenzo’s idea of a critical period to explain that within the first three to six months a child develops certain characteristics and therefore must create this mono Topic relationship within that time and this monotonic relationship also affects the internal working model which is a mental model of the world to help direct and control an individual’s environment effects these social releases.
So see these are social behaviors designed to elicit caregiving and lead to attachment and then you’ve got the continuity hypothesis which is the idea that emotionally secure children go on to be emotional adults whereas if they’re emotionally in central children they will be more like well to be emotionally insecure adults it was is thought that it’s preferably a sensitive period long and rather than a critical period.
So I mean it’s so in that sort form it’s important to get the monitor population than the three in six months but it’s not necessarily essential and obviously, this does not include the idea of multiple attachments which we spoke about earlier Mary Ainsworth did a really great study
Types of attachment (Mary Ainsworth)
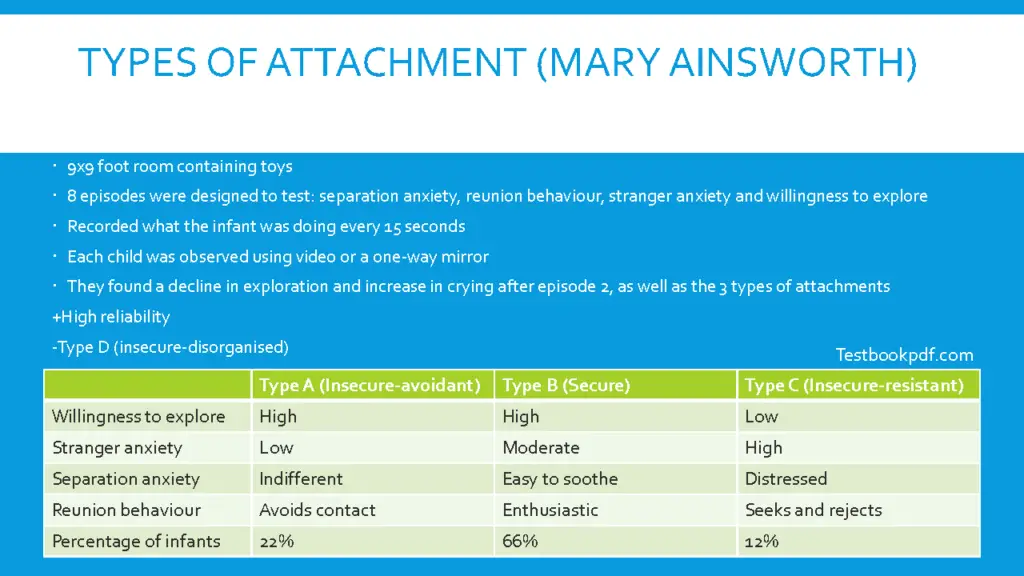
So she studied 106 middle-class Intamin infants aged 9 to 18 months and a nine by nine-foot room containing toys this was designed to be a strange environment and their episodes and eight episodes were designed to test separation anxiety reunion behaviors strange anxiety and willingness to explore and the behavior in the infant was recorded every 15 seconds each child was observed using video or in the one-way mirror and they found the decline in exploration and increase in crime after X 18 and then the findings also helped me to the three types of attachment that Ainsworth developed obviously this is high reliability however there is the idea of the type D attachment which is insecurely disorganized which is a mix which is a combination of type A and type C.
So yeah looking more at the type that I’ve got a table there I’m not gonna go like super through it light in depth because you can it is fairly easy to just look at and self figures out ideas from it but I will just say the type B which secure was the most common and then it was typed an insecure-avoidant and then type to see you kill resistant.
Cultural variations (Van Ijzendoorn and Kroonenberg)

So Cultural variations (Van Ijzendoorn and Kroonenberg) investigated inter and intra-cultural differences and they looked at a meta-analysis of 30 studies of the copied that repeated the same process as aimed worth leaders looked at so they looked at two thousand strange situation episodes over eight countries I found cure attachment was most common in all countries insecure avoidant was second most common except in Israel and Japan which are collectivist cultures they tend to focus more on being involved in groups but variations within cultures were one and a half times greater the variations between punctures which I think is really really interesting.
Bowlby’s theory of maternal deprivation

So deprivation and lots of emotional care that is normally provided by a primary caregiver could cause an emotional disturbance if it occurs before the age of five with no mother substitute.
So Bowlby studied case 788 to organ and clinic 444 of the worth beads of some degree.
So this study is often known as default for new study 40 mil of these were affecting Psychopaths as they lacked affection shame and a sense of responsibility and 86% of these 14 had frequent separations from their mother was their younger and 39% of all the thieves are all 44 experienced early separations long-term consequences also involved emotional maladjustment and mental health problems it’s obviously this core real-world application because it can impact how we care for children in the social system obviously there is the debate of deprivation versus privation.
Effects of institutionalization (Rutter and Songhua-Barke)

So effects of institutionalization studied by muttering song Gaurav arc I think I probably said that wrong but so Incisionless institutionalization is the effect of institutional care on an individual which and it can cause deprivation organism alone IQ insecure attachments and they tend to grow up to be poor and parents themselves.
So Rutter and song bark studied a hundred sixty-five children from Romania Institutes 111 who were adopted before the age of two and fifty-four were adopted by the age of four and then physical cognitive and social development were tested for the ages of four-five eleven and fifteen and the results were then compared to fifty-two British children adopted before the age of six months at the time the adoption remained that all the remaining children behind on all of the measures there’s been think they were fallen behind on the physical cognitive and social development by the age of four those who are adopted fourteen years old had caught up to the British children will have degrees but those adopted later still had felt issues with peers and had disinhibited attachments.
So again just has a real-world application because it can be used to help improve the care system but obviously, this behavior could be affected by looking more at the nature-nurture and debate.
So see deprivation is only one factor these children might have naturally just have slightly more disability detachments due to their genetics and how their parents learn things.
Influence of early attachments (Hazen and Shaver)

This behavior influenced boy Bobby’s internal work worrying include childhood friendships poor parenting remote relationships and mental health they got responses from 205 men and 415 women too and love Quinn in an American newspaper and they asked about current attachment experiences attachments and childhood and attitudes towards love and it found that 56% of them had secure attachments with which is the positive internal working model with average relationships lasting ten years twenty percent had an insecure-avoidant attachment with average nation thousand six years and nineteen percent had insecure resistant attachments with average relationships lost in five years obviously there is the issue with just the sample because obviously, they were volunteers sorry they were volunteers obviously they would make.
So okay doing that thermos in America only and there are a lot more females doing it than men and then obviously we have information in terms of their attachment types and the average relationship lasting this could be just like correlational Roth and causation like then they although that they were correlational and there is a positive correlation with them, it may not necessarily actually mean that these attachments are affecting how long they stay in relationships.


