Foundational Assumptions of Cognitive Psychology
In this article, we will give you full info related to Foundational Assumptions of Cognitive Psychology, The beginning of the article touches upon the concerns associated with studying mental states and processes that are non-physical. Later, the article focuses on behaviorism as an approach that aims to define solely physically observable events and processes.
We’ll also examine the behaviorists’ assertion that human behavior can only be fully predicted by its physical antecedents?
So, The title of today’s article is the foundation assumptions of cognitive psychology. Today I will be talking to you about the foundational assumptions in cognitive physiology to explain to you the principles on which scientific inquiry is based cognitive physiology. It is pretty much like playing a game and knowing the rules of the game before you engage in the game, in early childhood days sometimes you move to a new area, and find new friends, you are getting into a new game. It always better to know what the rules or the integrity of the game are before you start playing it, it is pretty much this to the same effect, and I will talk about what is the foundational assumption of cognitive physiology and why are they so, Let us start with the most basic question again
What is behavior?
If you remember the Article on introduction to cognition you would remember that I told you that behavior could be very simply just a stimulus and a response association so there is a stimulator and there is a response to it.
For example, somebody pricks you, with the pin and you take your hand back and you move away from the needle that Is pretty much what the simplest definition of the behavior could be.
What causes behavior?
Now the cause of the behavior is something that is slightly more complex to understand.
For example, the cause of behavior could be simply just a reaction, as you can say in the apprehend the needle example, or it could be motivated, by some internal desires.
For example, you want to have ice cream, or for example, you need to drink water because you are thirsty, So behavior in that sense can have caused on multiple levels we will see how this pan out while you are talking about cognitive physiology.

If you remember the definition of cognitive physiology, we would be talking about cognitive physiology as the scientific study of the mind. Now again this term mind comes in, and this idea in itself is slightly counter or has been slightly a counter lot of people because when we say mind, we are talking about something which is actually non-physical. Something rather abstract.
So the whole point of cognitive physiology is that we assume or that we build our discipline on the bases of this assumption that there is this world called the mind and where mental processes take place, where the mental activity goes on.
Also, this is the space where each and every element of the outer world is actually represented so you might have represented your dog, your sibling, your parents, or say simply for example a representation of where do you live, what are the objects that you use, and those kinds of things. Unless you have a mental representation of those things you will not be able to talk about those things in any meaningful manner. So in that sense, cognitive psychology is resting on this distinction between the inner and the outer world. We will try and see how we can approach this dilemma, and how we can talk about this internal world, in more scientific ways.
So without this actually to you know, achieve that feet it will be important for us to get some kind of the philosophical understanding of what this inner world, and what this material world means, The first concept that you like to understand is the concept of abstractness.
What is abstractness?
Abstractness is when you define something without a reference to the material world, without reference to the physical object that is there in the material world, thought believes, emotions, etc are all abstracts, because while they describe people sometimes describe aspects of this material world, they do not need those material aspects to exists.
For example, you might have the feeling of love, or you might have the feeling of guilt or shame about something or for someone, but this does not need that material entity to actually feel that or understand that the feeling of love, or feeling of pain, So that, is something which you will need to keep in mind.
However, you see that it is very easy that we can talk about and theorize about these abstract entities. This is something we always do, we always talk about our feelings, we always talk about how our feeling at any point in time, how something looks, those kinds of discussions we always have.
Why should be so easy to do that?
Probably because we understand that distinction between the physical and the mental, we understand what is the physical world we understand what is the mental world. And that is why we can talk very easily about these two things. Consider this statement.
For example, William decided to make a sandwich because he felt, hungry.
Now if you note, there are two important factors here the aspect that Williams is feeling something which is hunger, and the aspect that William is deciding something that he will make a sandwich. So how is it happing the two mental events are feeling and deciding to lead to the physical event that is making of a sandwich, this is something we are going to talk about in cognitive physiology in more detail?
However, as you will see it is quite possible to talk about these mental states and processes, in the absence of any discussion of any physical station process. We do not talk about that in the brain something happens and somebody decided, felt something or say for example that area of the brain decided, something so we not talking about this, physical substrates which might underline behavior or those kinds of thing. We will talk about how this interaction can be approached, as we move ahead in this particular chapter.

So in other words for the cognitive psychologist or cognitive psychology, it should be possible to proceed at the mind is an abstract entity with the only implication that it can be discussed and defined without reference to physical states and processes. So we have to begin, and this is the foundation assumption of cognitive psychology that you need to understand that the mind is metaphysical, the mind is a mental entity, it is not a physical entity. The brain is the physical entity we will come to the relationship between the mind and the brain but cognitive physiology rest on this distinction between the mind and the brain.
So this is one which you need to keep in mind before we move further.
Now if you understand this if you accept this that minis the mental entity on we are going to talk about that we are going to trail and investigate that, then as cognitive physiology was you should do is cognitive you could just you know develop theoretical models and develop an explanation of human behavior based on that physical entity. You do not really need to talk about what are the physical processes that are going on between your ears, you do not really talk about how the neurons are hiring, how are, the neuron transmitters acting, you cannot just talk about it completely, theoretically about what the particular mental function is, for example –
- what memory is?
- what learning is?

It is not to say that cognitive psychologists are not concerned with the neural structure at all or the material explanation at all, it is that they can exist without them as well. You will see as we go ahead in this course, that there is always an attempt to locate or to you know base that physical that metaphysical or mental explanation on the physical structures that are there in the brain.
Now moving slightly on a different plane an important question could be that science is a field, which is concerned about the physical world, it is concerned about measuring and it is concerned about the explaining, explaining things that happen in the physical world. So how can you science to talk about the mental world, how can you use science to talk about something that is entirely metaphysical? So we will see, and if we can talk about it at all.
what could be methods that we used to talk about this?
So we will go ahead with this we will see this physiologist attempt to understand human behavior and assume that the large component of this understanding requires the detailing of how this mental world pans out, A very inserting suggestion could be to read, how the mind works in which he actually really, interesting way approaches this topic.
I will take you to an alternative account. Now as I said science is basically about measurements and it is about really measuring the material and solid facts, there was this account of mental activities or human behavior which is known by the name of behaviorism. You saw in our history, Article on the history of cognitive physiology Article that behaviorism is one of the things that lead to the formation of cognition, it was in reaction to behaviorism that will not of cognitive physiology really comes up okay.
So let us try and understand behaviorism in a bit more detail today, Behaviorism is the view that the true science of psychology strives to achieve a description of human nature in terms of loss of behavior. You know, simply like for example loss of gravity, we have a loss of action and those kinds of things.

So the idea in behaviorism is that we must strive to generate a loss of behavior in terms of physical events and physical processes
Now these losses basically will contain statements only about observable things okay, you can make a law about only the things that you can see that you can measure only then you will be able to reliably predict everything, or so is the belief
For example, loss of motion or gravity or something like that.
Now the eventual theory of human behavior in behaviorism should therefore contain these universally established principles and should be able to correctly predict behavior. So if you talking about the physical world, say for example much like physics, if you understand the behavior of two objects or two materials you should be able to really and confidently predict that when these two objects are brought close two each other how they will interact or how they interact will pan out.
Edward Thorndike
Pretty much that was the idea about how psychology should exist as a science, as a field of inquiry. So for instance there was the law that any given human/animal will seek pleasurable things or un-pleasurable things, you know very simple assumption, and given two outcomes the human will always choose the pleasurable outcome over the un-pleasurable outcome. This is basically what the law of effect is. We discuss these this was given by Edward Thorndike.
In the last class. Edward Thorndike said that animals or humans will learn the response that leads to rewarding consequences and unlearn the response that will leave to punishing consequences. You know pretty much other simple you know the prediction of this because this effect of making a particular response leads to learning.
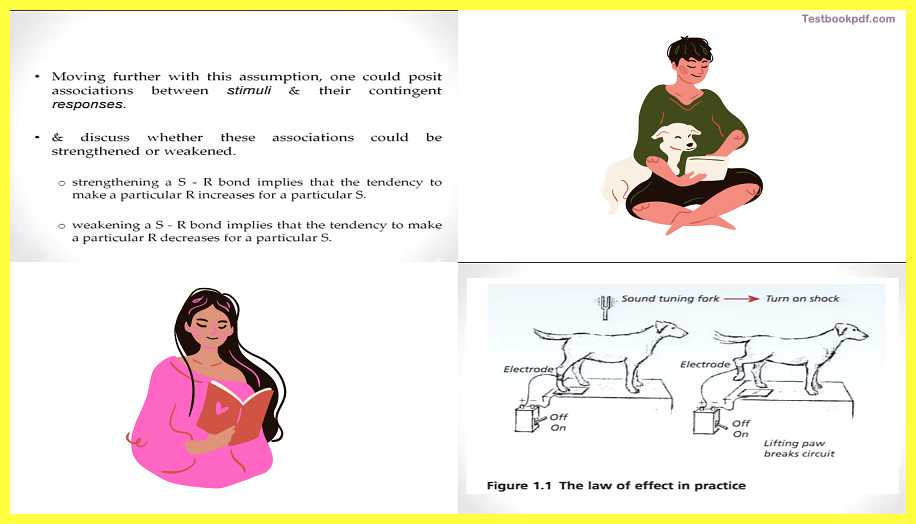
If you do something that leads to positive, you will do it again if it is something that leads you to negative reflects you will not do that. Pretty much this was thought to be, you know micro of all human behavior. We do everything that leads to good consequences, and we do not do things that lead to bad consequences. Now that should ring a bell, this statement should ring the bell, that is it so does it always happen like that, you know in that feeling that you will get when you say this statement again, that is where this crux of cognitive physiology use, we will see this as we go ahead, So if we further with the same theoretical model that behaviorism gives the whole idea is that behaviors is can be explained between the associations of stimuli and their cognitive responses, there is the stimulus and there is a response, that is pretty much all worth is the there to explain behavior okay. So stimulus-response bond is basically, that the tendency to make a particular response increase for the particular stimulus if you trying to strengthen this bond. If you trying to weaken this bond, that tendency to you know give a response R to particular stimuli S will decrease, and you can change or manipulate this strength to go on in further predicting human behavior that is what they wanted to do.
Take this example –
Here you will see that dog is connected to the set of electrodes and the wooden plane does also the metal seat, if the dog keeps its legs on that metal seat what can happen is that you can know have a sound of the tuning fork. When the sound of the tuning fork goes a dog receives a shock, over several trials when you do this, whenever the dog hears the sound of the tuning fork, it raises its leg, because that will break the circuit, and it will not receive any shock. And the point is of teaching the dog to learn this association between the tuning fork and the shock okay. This is pretty much a very simple explanation of behavior,
For example, you can still you this behavior to explain the use of this model to explain the behavior of various small children, animals, or those kinds of very simplest scenarios.
Principle of Associationism

Associationism talks about the feds of frequency and regency. If two are frequently occurring together you might link them, or if two things are occurring close in time together you might again link them okay.
For example –
How frequently a criminal is punished after committing a crime can teach him not to do a crime okay, if it is 100% of the time that the criminal receives the punishment after doing a crime he might not want to do it, or also how quickly a criminal gets punish after he done a particular crime. You know these kinds of associations can be made and that can lead to learning of a particular kind of behavior.
So useful learning then can take place from being able to either register the contiguity or register the frequency of co-occurrence of stimuli together. So what humans probably are doing, there registering this contiguity and this regency of these stimuli in this external world, and that is how we are shaping our entire behavior, that is what is supposed to be the behaviorist model of explanation of human behavior.

So learning then depends on the ability to register this co-variation of stimuli and their corresponding responses. So this is a practical way of explaining behavior, it supposes to be a scientific way of explaining behavior. But certainly, there are some problems with it, certainly, there are some side notes when would like to make when you are giving this kind of module, let us talk about those things.
So an association formation provides a straightforward account of learning about causation, you know we are always concerned about knowing the cause of how things happen in this entire world okay.
For example –
If event B is always following event A in close temporal proximity it might be reasonable to predict that A causes B okay, whenever A occurs B will follow, closely in that A is causing B to happen.
For example, you are taking aspirin and your headache is going away, if it is happen 100% though time will rather quickly after taking aspirin you might believe that the cause of aspirin is the effect of the aspirin is going away of your headache, that is another simple model what will see is that the story is slightly more complex than this.

What behaviorism is trying to say?
So let us take a moment and see how this is panning out. Now applying these principles of associationism and behaviorism, the behaviorists had hoped to show that behavior could be predicted and controlled, you can reliably predict how the person will behave in particular circumstances, or taking it further, you can also control how the person would behave in the particular circumstance. Now that was the program that is called the behaviorist program.
Animal experiments were then conducted in large numbers in controlled environments and their behaviors were predicted, because of knowing the previous history of re-enforcement and applying the loss of behavior. This is pretty much this is something that which gain a lot of popularity, in the early 1900s and pretty much like becoming the flavor of physiology, nobody wanted to talk about mental states and stuff like you know there is something called the mind. Because it was giving a rather reasonable, job of explaining simple behavior, people were not talking about, their mental state so much at that point in time.
So ultimate goal was to the result of this animal experiment, to the whole of human society, and hence provide the theoretical framework for explaining and understanding human behavior.
If you remember in the history classes telling that skinners idea was if you give me a set of individual, and if you give me a right condition to raise them, I can make them run out whatever you ask me to, I can make them be run lawyers, you know artists, actors, whatever. This is the kind of confidence they had in this theoretical framework.

Note, however, that an explanatory concept for behavior mind is not being used, mind they are not talking about, mind at all. An implication of this whole exercise could be that you know animals and even humans are considered only nothing more than machines.
For example, if you know a machine you press a particular button a particular response is got 100% at a time, this is pretty much what they want to say and what are moving ahead with. That the point that has been conveyed here if you focus and think of this update, is according to behaviorism human behavior is seem to describe in terms of a deterministic system, in which everything happens all the time with 100% certainty, you do you have a stimulus you will have a response be and then will happen 100% of the time. There is nothing that can change it okay, it is almost as good as the machine.
human behaviorism
So as with any other machine as long as we can identify the physical antecedents to some form of behavior we can then claim to understand the causes of the behavior. So if you study that what led to the particular behavior if you study that there was a situation was like this, you know something was said, somebody did something, that was led to particular kind of behavior, and this pretty much very comfortable way or simple way of understanding what human behaviorism is about, Is that an oversimplified model, or is that the model, or is that the model you know explains all of human behaviorism, something that I leave to you to think of okay? So in other words behavior could be defined fully by its physical antecedents.
Now such an account is basically in line with all other scientific theories of the world okay, physics, chemistry, even biology, and all other strong nature sciences that you would say wherein the whole paradigm is that certain causal variations link objects and events and the occurrence of the causal antecedents can practice future action.

If you have an X and Y condition of the temperature and pressure and volume you can reliably predict how a particular material behaves in these situations. This is pretty much what human behavior was about much like a wall clock you know in winding up a wall clock the rotational energy applied to the key, is stored in the internal spring and the release of this energy is basically what results in the hands of the clock rotating, is this a satisfactory module of or satisfactory explanation of human behavior is something we have to think of, This pretty was called methodological behaviorism, and this is basically a term which was given by Searle. In behaviorism if you have been noticing till now there is no room of free will as they aim is to provide an account of human behavior that wide any mention of decision making or choice okay.

So you can not want to do something, and you have not had a desire to do something unless the physical antecedents permute you. So these physical antecedents will completely determine how your behavior will be in a particular situation, that is what the behavior explanation is. Behaviorists also limit themself to describing behavior solely in terms of these determinates principles, the law of effective learning, reinforcement, and punishment these kinds of principles.
Now so, the behaviorist stance then is, to sum up, the theory of behavior defines respect to set up to the loss of behavior, and the aim of behaviorism is to uncover these losses in order to predict and control behavior, Any theory that terms of explains human behavior should only contain statements about observable objects and events okay. So this kind of behavior was reinforced for this amount of time, that is why it really too particular kind of human. That is what they were talking about.
Logic behaviorism

Now coming to a different flavor of behaviorism which is Logic behaviorism, logical behaviorism was actually a more radical stand that was taken by behaviorism. Logical behaviorism is basically rules out the discussion of anything but observable events and entities in our account of behavior. So it says unless you can observe a measure the antecedents you cannot use those to explain behavior. Anything that cannot be observed should not be the figure in this you know the whole contact of human behavior.
Now also logical behaviorism it aims to redirect explanations, any mentions of mental states, or processes in a bit to focus only on observable entities that is pretty much what logical behaviorism pushes for.

So consider this statement, I say William is trusty and another statement is if there was water available then William would drink okay. Now according to logical behaviorism everything you wish to predict from saying that William is trusty because thirst is an unobservable mental state can be accounted for by stating a statement to if there is water William will drink it why do you need to say that William is thirsty okay, that is what the logical behaviorist stance is okay. And this thing they basically refer to the behavioral deposition if there is water available I am disposed to make use of that water, by drinking it okay. It is not I do not need to talk about that, you know I am thirsty I feel that I want to drink water nothing like that. If there is water I will drink it and that is pretty much those simple explanations.
Now Logical behavior is basically preferred statements like this, because they do not have to mention of anything unobservable, thirsty, feeling those kind of things are not really there.
Let us take another example, harry believes it will drink, harry will be the other two sides that will be, harry will be disposed to wear a raincoat and take an umbrella and he goes out.
Churchland

Now Churchland notes that such a behavioral perspective which we talked about of this logical behavior is mentioning mental entity is nothing more than is shorten the way of talking out potential patterns of behavior. So if there is going to be rain, and if you know there is going to rain you will be disposed of taking an umbrella with you. It is not like you felt like take an umbrella, or you wanted to take an umbrella, do not take about those things talk about that if there is a chance of rain you are disposed of using an umbrella with you, that is very much what that the behavioral is really wanted to pose, As this has been considered to be the challenge to the cognitive position.
Now you can see that from this position, you can actually know in some sense you really wonder whether you need to talk about mental activities or mental functions at all.
psychology Dispose of Meaning
There was a certain decision to the logical behaviorism; we just visit them for a short while.
For example –
Let us try and analyze what disposition really means okay, you say that harry disposes of rainwater or harry, or William is disposed to take an umbrella, what does this disposing thing really mean. Harman basically knows that whether you dispose to take an umbrella with you depends, on not just your belief that it will rain, but also its desire, not to get wet, and your perception of the umbrella, in the corner and you further believe that umbrella is good for keeping the rain off, and so on.
Now you see this statement really has so many references to what basically the logical behavior is would not like, you know the belief that it will rain and the desire that you do not want to get wet, and the perception that there is an umbrella. And again the belief that the umbrella is good to save you to from getting wet. So even if you try and explain the disposition you really you know making use of things which are abstract, things which are mental entities. S you cannot really escape from these from the mention of these mental entities is by just talking about this analysis in terms of dispossession, which is one major criticism of logical behaviorism.
Another objection to logical behaviorism is made by Searle, and Searle says and he basically raises a very interesting question, he says that can you talk about that means to be human, and you know without really talking about the ordinary experience, of what it is like to be a human being, For instance, can you really explain our human behavior without mentioning our thoughts and feelings? So we do not really go to say that I did this or I did that, we generally talk about that okay, you know I felt something feeling, sad so I went and did this for that feeling very happy, so I went did. But generally in a mood naturally, level our explanation of behavior rests on these mental entities, rests on these abstract concepts. And pretty much this psychology has to do a good job of explaining mental human behavior, it needs to take in these accounts, it cannot survive without talking about these things okay. That is a very interesting observation to make.
For example, Searle says how do you describe you know the aspects of to be religious, you know how do you say that you know X is religious, what is the aspect of religious, you know that thing is being religious only a collection of dispossession such as.
For example, if there is a temple I am disposed to visit the temple, and if there is a mosque you know I am disposed to pray in the mosque is being religious something entirely different which is again something that exists in your mental space exits in your abstract world.
Now if you see these two criticism of logical behaviorism by Searle and otherwise are very found it, and this is what lead gradually to the response that we see as cognitive physiology okay, this is what takes us to the fair that cognitive physiology should be there, and we will talk about how that happens, Consider this example logical behaviorism would have us believe that to have pain is nothing more than to be inclined to wince or to take an aspirin, etc.
Now if I tell you that you know you come to me with pain, you know you got hurt in your foot or something and you say that you have a lot of pain, and I tell you that it is not that you are having the pain or anything you are just in client to take an aspirin. That does not seem like a very good explanation, and I am sure it is not going well if you tell somebody this, So this is in some sense you know overall or the basic shortcoming, in behaviorism which we will see how gradually leads us to the whole explanatory framework that is called cognitive physiology.
Summary

Let us sum up what we did today in summary logical behavior is a substitute statement about mental states and processes, and statements about dispositions and to behave in certain ways, yet in attempting to explain all of the human behavior in terms of these behavioral dispositions, these approaches face to acknowledge that as we human beings, we are sentient beings typically act in ways that are determined by our thoughts and feelings which are not our physical entities, which are mental entities. So we are pretty much always taking into account the mental world. So thank you for today we will go in the next Article to the cognitive position, we talked about the behaviorism positions today thank you.
Read also:
A Brief History of Cognitive Psychology Theory, Example, Pdf
A Brief History of Cognitive Psychology Theory pdf (Part-2)
Click here for Complete Psychology Teaching Study Material in Hindi – Lets Learn Squad


