Behaviorism Psychology Theory, Examples, Images, (Pdf Link)
Hello, learners today I will give you Full Information About the Topic of Behaviorism, Behaviorism Psychology Theory, Examples, Images, (Pdf Link), and behaviorism as an approach to learning with examples.
Behaviorism as an Approach to Learning
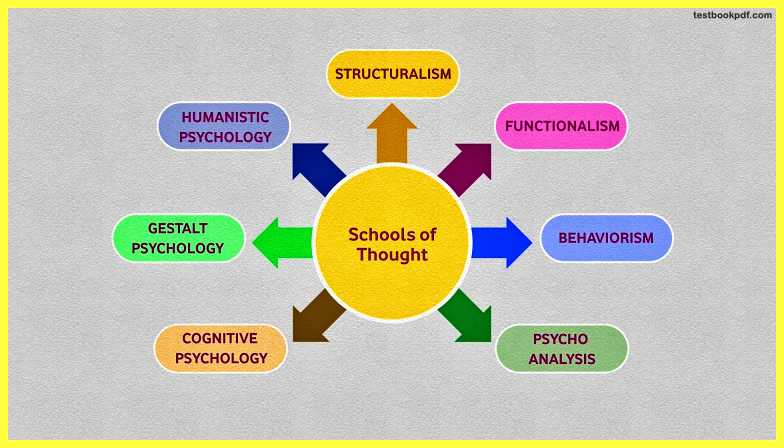
Let’s Start From the Beginning. As we know that psychology has different schools of thought that have influenced our knowledge perception and understanding of various aspects of psychology.
- Structuralism: the main school of thought is structuralism through which psychology tries to understand the structure or track listings of the mind.
- Functionalism: which deals with the nature of the mental state.
- Behaviorism: emphasizes the learning of behavior.
- Psychoanalysis: there is another school of thought psychoanalysis that deals with the study of unconscious mental processes.
- Cognitive psychology: cognitive psychology mainly deals with the scientific study of mental processes.
- Gestalt psychology: we have a different school of thought which is Gestalt psychology which emphasizes on mind and behavior as a whole.
- Humanistic psychology: humanistic psychology looks at an individual as a whole.
Out of these schools of thought today I will discuss I’ll focus only on behaviorism, first of all, a question comes to our mind.
What is behavior?
Behavior consists of reactions and movements that an organism gives and does during a certain situation, according to the behaviorist approach nobody is good or bad from birth it depends on what kind of environment experiences and situations one is getting, and accordingly, behaviors are acquired, now the next important concept is behaviorism.
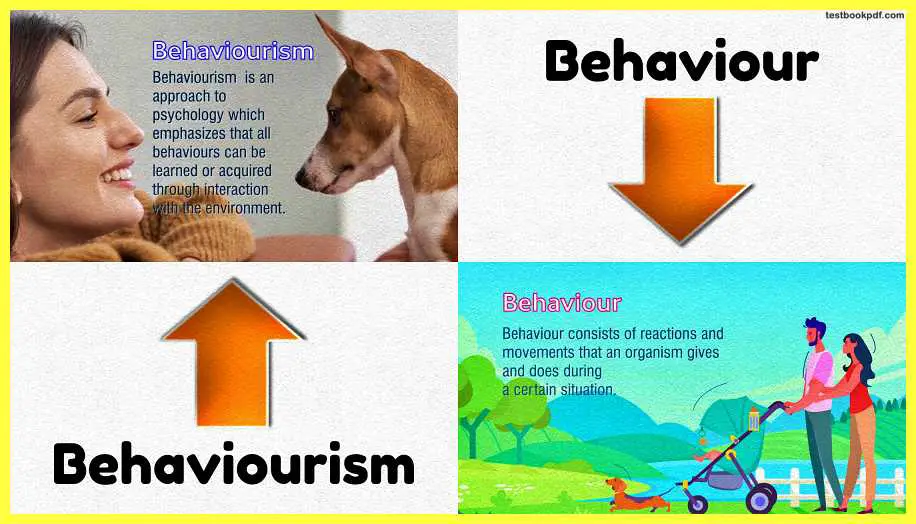
What is Behaviorism?
It is an approach to say ecology which emphasizes that all behaviors can be learned or acquired through interaction with the environment, if we look back into the history of the behaviorist approach there was An article psychology as the behaviorist views it, this article was written by the famous psychologist JB Watson who is also considered As the father of behaviorism in this paper he outlined behaviorism as an objective branch of science he clearly states that it is not scientific for psychologists to study an observable phenomenon rather Miserability and observability of human behaviors are more important, now this concept of behaviorism is very helpful when we take it as a source of learning.

Behaviorist’s views of learning
Behaviorist views learning as a psychological approach to learning which is mainly based on the idea that all behaviors are learned through interaction with the environment, the behavioral view generally assumes that the outcome of learning is changing in behavior and as the interaction takes place with the environment, therefore, external events of the environment also have an impact on individuals learning, it means the kind of experience any individual is getting in a particular environment it affects the learning of that individual.
Basic Assumptions of Behaviorism
Now there are some basic assumptions of behaviorism as an approach to learning.

Points of assumptions:
- Environment plays a key role in the learning of all behaviors: it means whatever learning takes place interaction with the is a necessary aspect.
- This approach is scientific in nature: it means that measurement and observation of behavior are important to point it, and it emphasizes the importance of observable behavior.
- There is a little difference in the learning process of humans and animals this is evident from the many experiments of behaviorist theories where animals were taken to the process of learning and their behavior was modified with the various laws of learning.
Behavior is the result of the Association of stimulus and response.
Now, these two terms stimulus and response are very important to understand if we want to see the association between these two terms
What is a Stimulus?
Stimulus is any event that activates behavior and response is, the observable reaction to that stimulus, so, there are many psychologists other than Watson who had contributed a lot to the development of the behaviorist approach as a source of learning such as –
- Ivan Pavlov
- BF Skinner (Burrhus Frederic Skinner)
- E.L Thorndike (Edward Lee Thorndike)

As per the behaviorist approach of these psychologists, the concept of learning is a process where the association between stimulus and response occurs, to understand the concept of this learning it is very important to discuss the concept of conditioning.
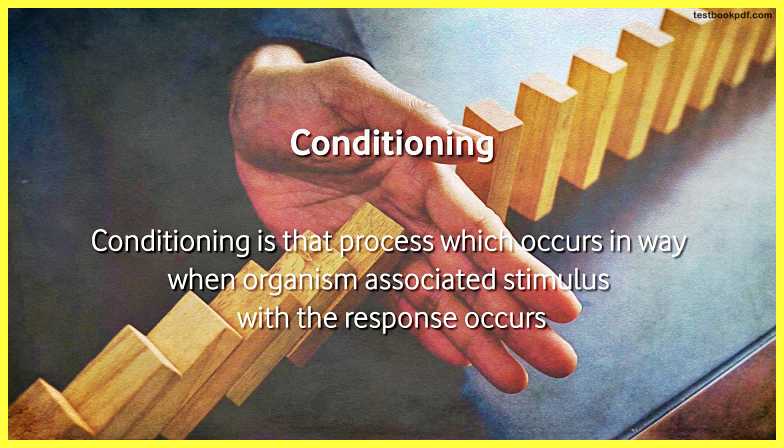
What is conditioning?
Conditioning is a process that occurs in a way when an organism associated a stimulus with the response, this process of conditioning can be divided into two types –
- Classical conditioning
- Operant conditioning
When we talk about stimulus and response Association it also indicates Towards the principle of contiguity which states that whenever two or more sensations occur together and repeat again and again they will become associated, further later on when only one sensation occurs the second will be remembered automatically to make this point more clear let us discuss the classical conditioning theory of learning given by Ivan Pavlov.
Classical conditioning theory
Classical conditioning theory describes learning by associations and helps in learning psychological responses such as fear, salvation or sweating, etc.
Pavlov through his experiments provided evidence of a form of learning based on the repeated Association of two different stimulate, there are many key concepts in this classical conditioning theory.
Pavlov’s classical and Operant conditioning theory with Image
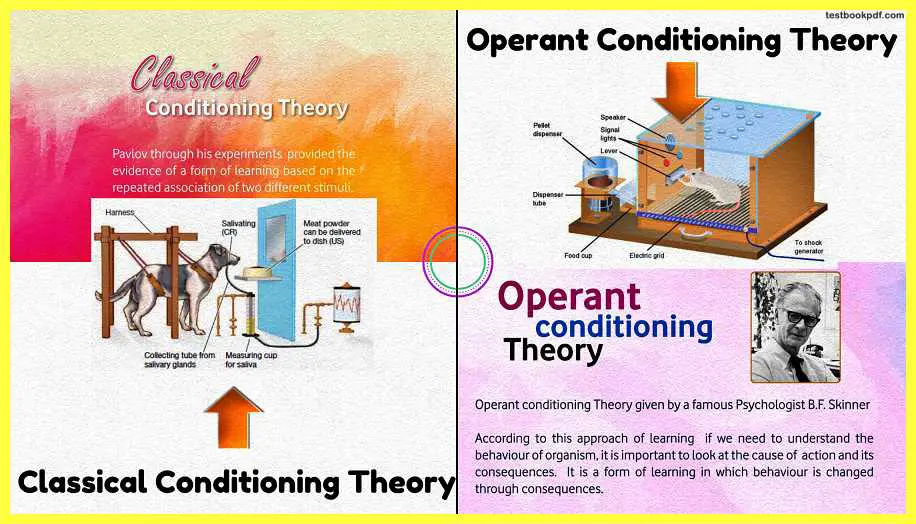
Pavlov’s classical conditioning theory with Explanation
let us understand this theory with the explanation of these points –
Unconditioned stimulus
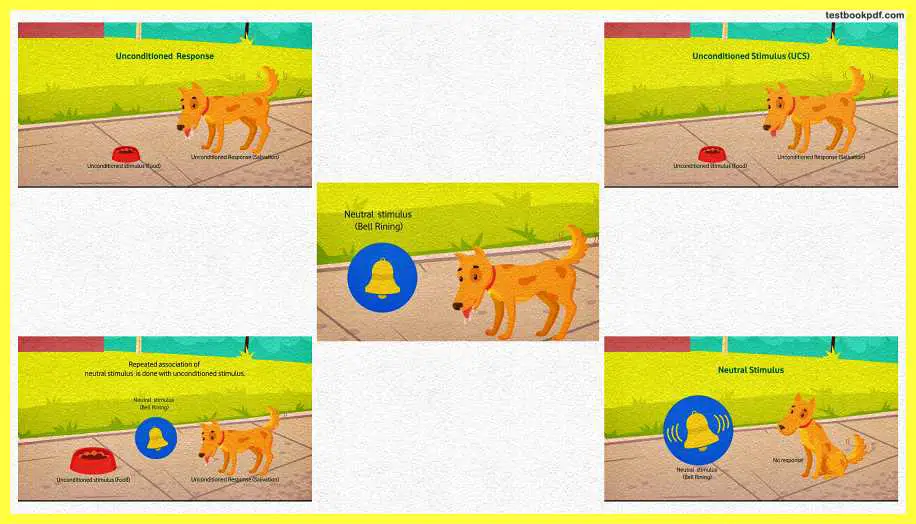
The first key element is the unconditioned stimulus, the unconditioned stimulus is any stimulus that constantly produces a naturally occurring automatic response, in Pavlov’s experiment the unconditioned stimulus was the food, which was presented to the dog.
Unconditioned response
The next important element is the unconditioned response the unconditioned response is the response that occurs automatically whenever the unconditioned stimulus is presented it means that it is caused by the unconditioned stimulus.
In Pavlov’s experiment meant unconditioned response was salivation which occurs because of the food given to the dog and this process is considered as the natural process that whenever food is given to the dog there is a natural response that Saliva will occur.
Neutral stimulus
Now next element is the neutral stimulus it is a stimulus that is not responsible for the desired response if it is not associated with an unconditioned stimulus in Pavlov’s theory sound of the well is initially considered as the neutral stimulus because there is no salivation in the dog produced by the presentation of sound of the bell.
Process of conditioning
The next important process comes to the process of conditioning which happened during the process of conditioning, The neutral stimulus was associated with an unconditioned stimulus and the same association was repeated again and again which ultimately results in conditioning, So, what happened in Pavlov’s classical conditioning theory, the sound of the bell and the food, the association takes place between these two –
Pavlov rang the bell first and then provided food to the dog so this combination was repeated, again and again, after the process of conditioning, there was a change in the status of neutral stimulus the neutral stimulus become a conditioned stimulus.
Conditioned stimulus
The conditioned stimulus is the stimulus that is neutral at the start but through repeated association with the unconditioned stimulus, it produces a similar response to that caused by and stimulus in conditioning theory the sound of the well becomes a conditioned stimulus when it’s repeated Association is done with an unconditioned stimulus.
Unconditioned stimulus
Now because of this unconditioned stimulus, there is a conditioned response the conditioned response is that response that is learned by the organism and caused by the conditioned stimulus, In this experiment of Pavlov, the conditioned response is this elevation produced by the dog when only the sound of the Bell is presented that time there was no food which means there was no unconditioned stimulus so it was the association between the conditioned stimulus and the conditioned response.
Mechanism of the whole theory
let us have a look at the mechanism of the whole theory.
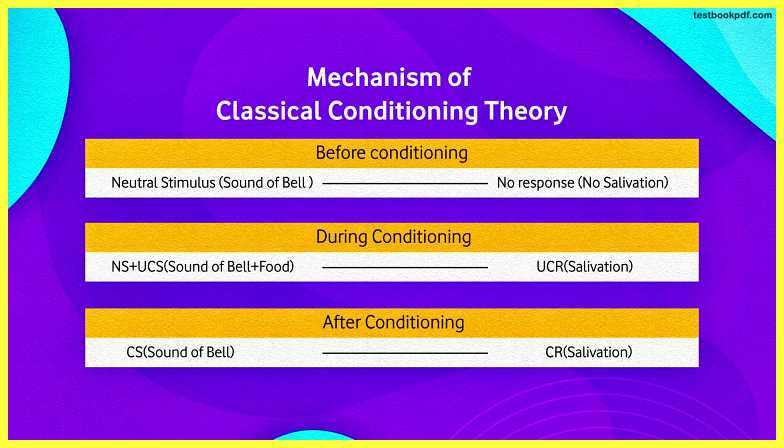
Before Conditioning
First what happened whenever a neutral stimulus was presented there was no response from the organism which means whenever there was this sound of the Bell there was no salivation from the organism.
During Conditioning
During the conditioning, Pavlov was done that he associated neutral stimulus with unconditioned stimulus and there was an unconditioned response that the dog generated the saliva and when this combination of this association of neutral stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus was repeated, again and again, there was a process of conditioning.
After conditioning
It means after conditioning conditioned stimulus which was earlier taken as the neutral stimulus produces the conditioned response from the organism, So this was the theory that emphasizes the behaviorist view of learning through the association of stimulus and response.
Operant conditioning theory
This theory was associated with behaviorism and is given by BF Skinner, according to this approach of behaviorist theory if we need to understand the behavior of an organism it is very important to look at the cause of action and its consequences it is a form of learning in which behavior is changed through consequences.
What is the nature of these consequences?
Nature of these consequences: the main point is that if the outcome is the consequences of any action or behavior are pleasant or successful find in nature there is more chance of repetition of the same behavior by the organism, whereas if the behavior is followed by unpleasant consequences there are fewer or less chances of occurrence of that behavior in the future, here the type and timing of the consequences can strengthen or weaken the behaviors.
The important point in operant conditioning
There are some important points like in operant conditioning behavior is first then on the basis of consequences it depends organism will repeat that behavior or will not repeat that behavior, so what happened in operant conditioning there is a very important concept of reinforcement, so if we want to understand how consequences can help in strengthening behavior we have to understand the concept of reinforcement which generally means “a reward”. A reinforcer is there for any consequences which help in strengthening behavior.
2 Types of Reinforcement
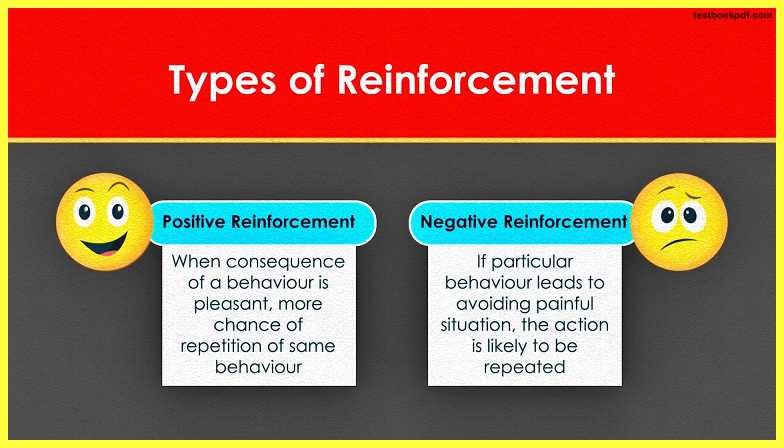
There are two types of reinforcement
- Positive reinforcement (+ive)
- Negative reinforcement (-ive)
Positive reinforcement with example
If we want to increase the chances of behavior or the desired response we provide rewards to the individual whose behavior we want to strengthen so, it is a kind of stimulus which helps to increase the probability of desired response
For example – in the teaching-learning process when we praise the students for good work or for their performance or sometimes we give a prize to the student for their performance there is a possibility that the student will repeat that desired behavior again in the future because of that positive reinforcement.
Negative reinforcement with example
In the case of negative reinforcement if a particular action leads to avoiding an aversive situation then that action is likely to be repeated in a similar situation and the process is called negative reinforcement.
For example – if we sit in a car and do not put the seat belt, there is a buzzing sound which will irritate us until we put on this seatbelt therefore to avoid that aversive experience we repeat the desired behavior, here it is very important to mention that negative reinforcement is different from the concept of punishment which involves in decreasing the behavior.
Punishment
So, punishment is the process that decreases the behavior, again punishment is of two types
- Type 1 punishment
- Type 2 punishment

- Type 1 punishment is a kind of presentation punishment where punishment is given on the occurrence of eye desirable behavior.
- Whereas in type 2 punishment which is removal punishment here pleasant stimulus is removed on the occurrence of certain behavior.
Conclusion
- On the basis of this discussion we can say that behaviorism has contributed a lot in the field of learning, it has mainly contributed to shifting the focus of psychology from the mentalistic approach to behavior
- It is also very useful in shaping the behavior of children and developing good habits among them
- This concept has also proved effective in developing positive attitudes and deconditioning emotional fears
- One of the important contributions to the development of programmed learning is a new methodology of teaching, therefore behaviorism is an approach that is very helpful in shaping the behavior of the organism and gaining the desired response from the organism
So, dear learners in this session we have discussed how we can acquire how we can modify and how we can bring desirable change in the behavior of the students through the association of stimulus and response thank you so much, If you Like this Post Please Share it with your Friends and Bookmark this Website Testbookpdf.com.
Read also:
All Psychological Perspectives Theory, Examples, Images, Pdf
Click here for Complete Psychology Teaching Study Material in Hindi – Lets Learn Squad



