The Cerebral Cortex Psychology Theory, Images, Pdf Download
The topic of today’s article is The Cerebral Cortex Psychology Theory, Images, Pdf Download, This article focuses on the structural and functional organization of the cerebral cortex, We will talk about hemispheric specialization and lobes of the cerebral cortex (Frontal, Parietal, Occipital and Temporal lobes) with respect to their cognitive functions and roles.
The Cerebral Cortex
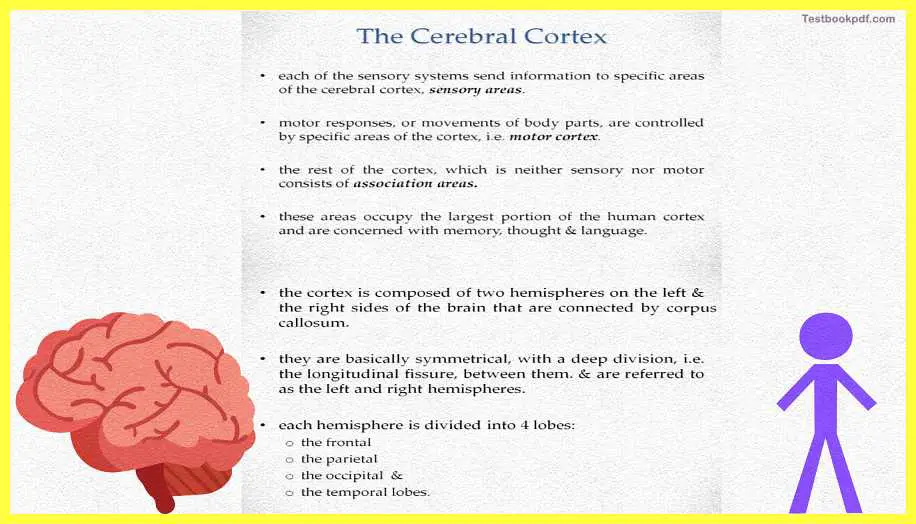
The cerebral cortex basically can be said to have three specific kinds of areas so each of these sensory systems, the systems of vision, audition, etc all of them send information to the specific areas in the cerebral cortex which are the sensory areas. Motor responses or movements of body parts are basically controlled by other specific areas of the cortex which are called the motor areas. The rest of the cortex basically which is neither sensory nor motor basically is a set of areas that are the association areas. These association areas basically acquire the largest portion of the cerebral cortex and these are the areas that are concerned with higher mental functions, which are like memory thought, and language.
The cortex is composed of two hemispheres one on the left and one on the right and these are basically connected together by a bundle of axon fibers called the corpus callosum. These areas the two parts of the brain the left and the right hemispheres are basically symmetrical and have a deep division wherein they are connected which division is called the longitudinal fissure. Each of these hemispheres is basically divided into four lobes, the frontal, the parietal, the occipital, and the temporal lobes.
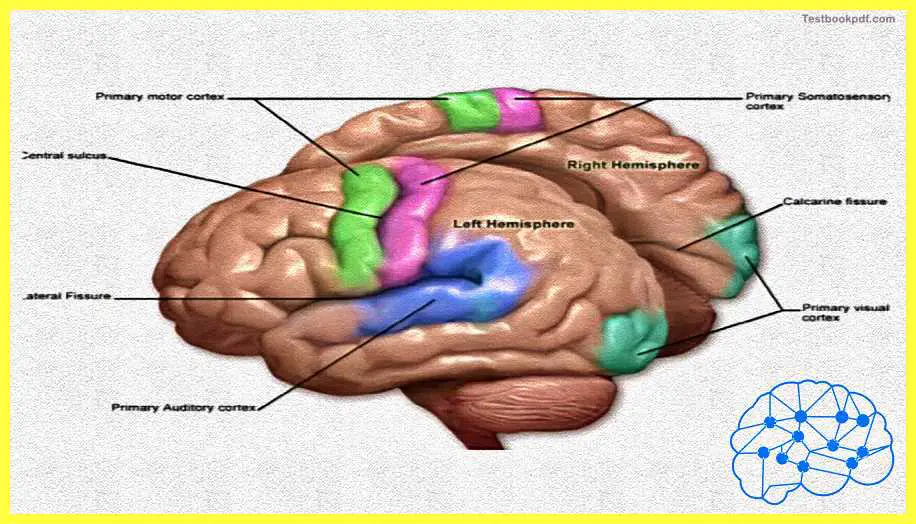
Both hemispheres contain homologous versions of these lobes. So the left and left and the right hemisphere will both have the frontal lobe, the left and the right hemisphere will both have a temporal lobe and they both will have a parietal and an occipital lobe.
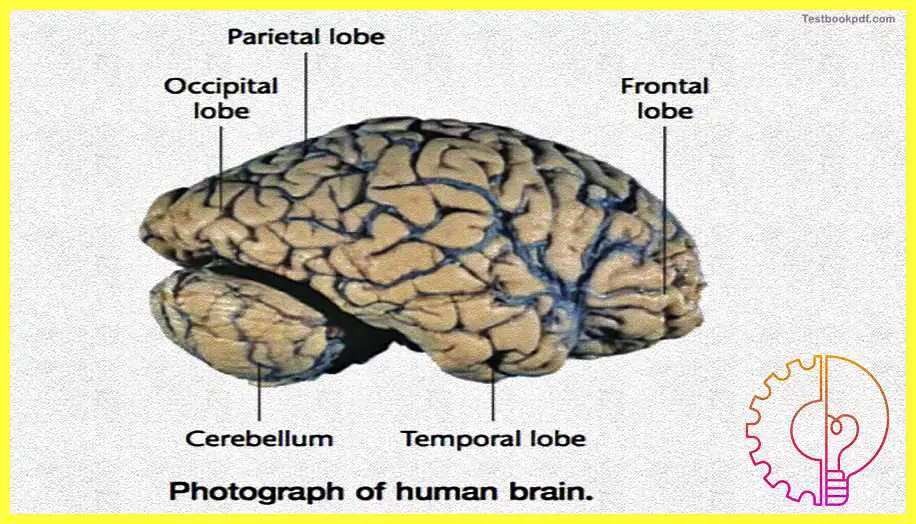
Here you can see in this figure that these are two parts of the brain which are the left and the right hemispheres. Both of these have the primary motor cortex, both of these have the primary somatic sensory cortex, and both of these have the primary visual cortex and the auditory cortex.
Here you can see in more detail that this is the layer of muscles which is called the tissue of the cerebral cortex. You will also see the division between the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe, and the occipital lobe. This is the real photograph of the human brain wherein you can more directly see where each of these lobes is situated.
The Cerebral Hemispheres
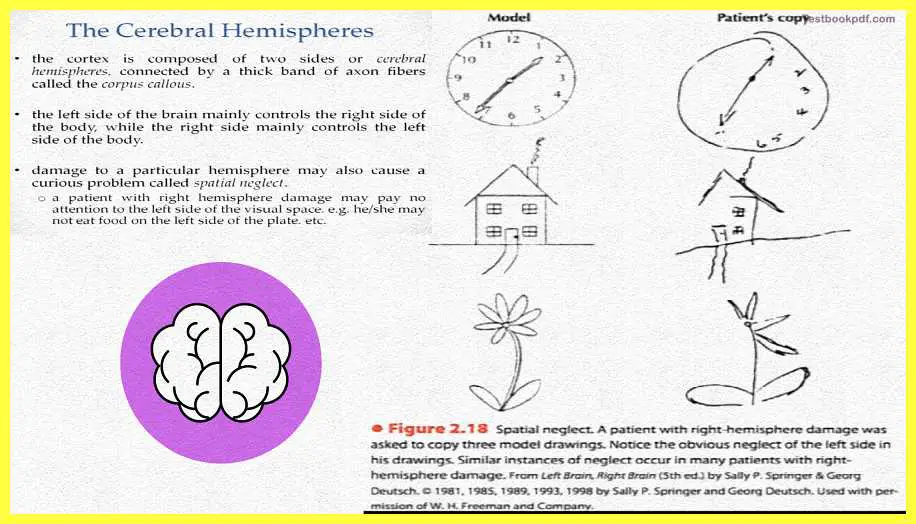
Now coming to the cerebral hemispheres, it can actually be seen to have these two sides which are the cerebral hemispheres, they are connected by this as I said thick band of fibers called the corpus callous. The left side of the brain mainly controls the right side of the body while the right side of the brain mainly controls the left side of the body. These are basically the basic principles of the organizations in the human brain.
Now damaged to one side of this vein, or damaged to one of the areas of the left hemisphere or one of the areas in the right hemisphere may also cause curious problems which say as example spatial neglect. Spatial neglect is an interesting problem in the sense that a patient.
for example, right hemisphere damage may end up in no tension at all to the left visual space because that is what it was supposed to process.
Interesting things happen, say for example a patient who has right spatial neglect or who has right hemisphere damage and has left spatial neglect might not be able to pay any attention to, for example, food on the left side of the plate or will not be able to comb the hair on the left side of the head and so on.
Here is the demonstration of the kind of figures that these people come up with so on the left side you will see the model which the patient was asked to actually reproduce, and you can see that the patient actually produces the numbers on only one side of the clock or similarly makes only one side of the house or only makes only one side of the flower, this is basically I was referring to when I was talking about spatial neglect.
Hemispheric Specialization
An interesting concept that is a very dominant concept in understanding, the brain is the concept of hemispheric specialization. Now hemispheric specialization is basically a concept that the two cerebral hemispheres may be differently adept in their capabilities and functions, for example, if you talk about mental functions like language or say for example perception or music or maths the idea that hemispheric specialization proposes is that one of the hemispheres is slightly better at say, for example, language or music or some other abilities.
An interesting scenario with respect to hemispheric specialization actually occurs with patients who have a split brain. The split brain is basically the patient who is those who have undergone a particular kind of surgery wherein the corpus callous is severed. So now it happens is the patients will have both sides of the brain pretty much functioning normally, but just the fact that they are not connected to each other anymore.
The Right and the Left Brain
Gazzaniga says that this kind of result is often in a scenario where is essentially one person with two kinds of brains or two brains. After the right and the left brain are separated each of these hemispheres will have its own perception, will have its own concepts, and impulses to act. And those will not be communicated to the other hemisphere in that sense not be integrated to lead to normal behavior.
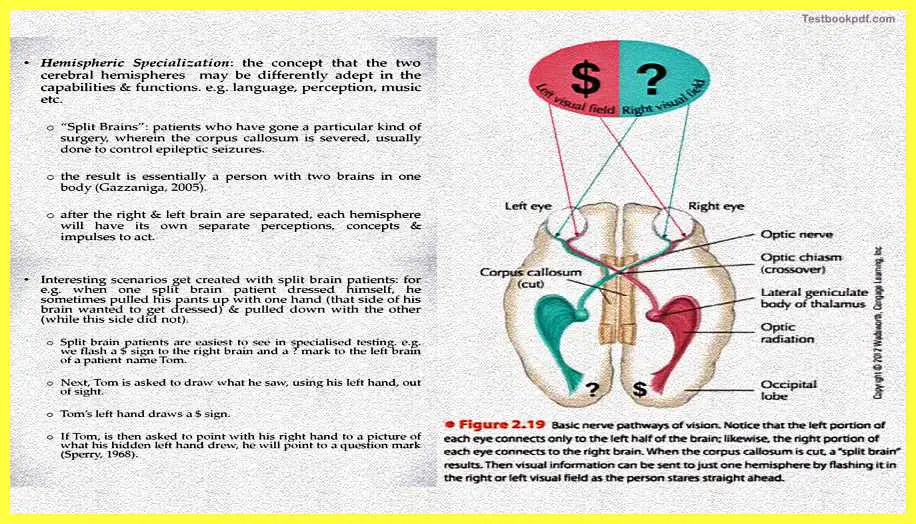
An example could be, that if you really want to test how the behavior of the split-brain patients is, so one of the experiments one could do is you could flash the dollar sign to the right brain and question mark sign to the left brain of a patient let us say named Tom, then we ask Tom to draw what you saw using his left hand while the left hand is out of sight, so you can actually cover the left hand you can ask him to draw with his left hand whatever he saw or he is seeing.
You will find it on the left hand of Tom will end up drawing a dollar sign which is basically a flash to the right brain. Because your right brain controls the left hand and in that sense from the left hand this person draws the dollar sign. Now intentionally if you ask him to point out with his right hand a picture of what is written and what the left hand might have drawn Tm would point out the question mark. Because now he is using his right hand he is basically going to point out something which the left brain has seen which is basically a question mark.
So you see that the perception of the two visual stimuli that we presented to the left and e right brains is so disconnected that one of the hemispheres does not really know what the other hemisphere has actually seen or experienced. This is basically a representation of the scenario that we were talking about so you present the dollar sign in the left visual field which is to be seen by the right hemisphere and the question mark sign to the right visual field which has to be seen by the left hemisphere. This is pretty much what we were talking about right now.
Now in this whole point of this hemispheric specialization let us talk about what is the unique abilities of each of these two hemispheres. Now I use the work unique which will actually not apply here because we say both the hemispheres of the brain are capable of doing or performing most cognitive functions the only difference will be more adept and it is a matter of degree actually one might be more adept one particular cognitive function while the other will be less adept. So it is not that the right hemisphere does not process any language at all and the left hemisphere processes all the language it is that the left hemisphere language process better in some components while the right hemisphere might process language in some other components.
Brain Percentage
Now, as I was talking about language, roughly 95% of us use our left brain for language say for example speaking the language, writing language, or understanding language. Also, the left hemisphere is found to be superior at abilities like maths judging time and rhythm, and also coordinating the order of complex movements, for example, if you have to do a highly dexterous task which was in the use of your fingers and fine motor movements.
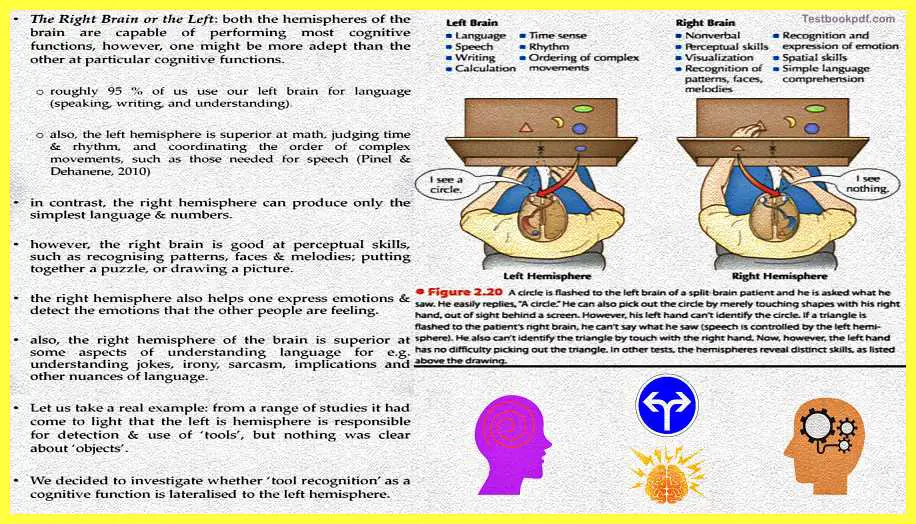
In contrast, the right hemisphere can produce only the simplest language and numbers. However the right hemisphere is good at other things, say for example perceptual skills, recognizing patterns, recognizing faces, understanding music, and drawing a picture those kinds of things the right hemisphere is supposed to be better at, I am not saying it exclusively does it again I am saying it is better at doing this. The right hemisphere also helps one express emotion and deducts emotions that the other people are feeling.
Finally, the right hemisphere is superior at some of the aspects of understanding language say for example understanding jokes, irony, metaphors, and those kinds of aspects.
So in this figure see a slight comparison of what the left brain and the right brain might be able to do, it is basically not supposed to be taken too seriously because both of the parts of the brain do each of these things it is just by the degree that says, for example, the right hemisphere is much better in non-verbal skills whereas the left hemisphere is better in language-related verbal skills.
Now let us take an example from one of the ranges of studies that I personally did and basically wherein we were trying to see whether the left hemisphere was involved in the deduction and use of tools but that kind of scenario.
What are tools?
Tools are those objects that we use in our hands to achieve certain things, for example, hammers, rulers, or things that we can actually pick up from our hands and use to create particular kinds of affairs.
So it is basically known, that it was already in the literature that the left hemisphere is involved in using and manipulating tools, while the right hemisphere is not or right hemisphere is not involved directly in the using the manipulation of tools. Less was known about the other objects say for example what happens with other objects like things that you do not use as tools there is no clear indication of that.
Tool Recognition
So we wanted to actually compare this and this was there, so we actually created a task which was called a visual half-field task which was basically specifically designed to investigate whether tool recognition is lateralized that is processed laterally by the left hemisphere or not.
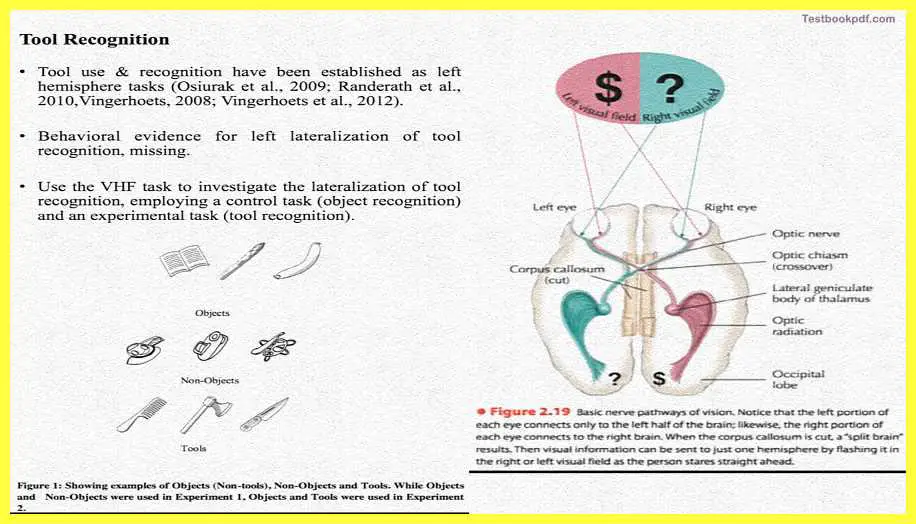
So we had a scenario pretty much similar to the one which we saw so we present something in the left visual field and we expected it to be processed by the right hemisphere we present something to the right visual field and then we expected to be processed by the left hemisphere.
So these are the kind of stimuli which we use so on the top you can see objects which are not tools and at the bottom, you can see objects which are tools which I actually refer to earlier, and middle we also had a comparison with things called non-objects, these are just random shapes which can be considered as objects but they are not.
Object Recognition Task
So had two kinds of the task we had an object recognition task in which the participants had to tell us whether what he or she was seeing as pointed by an arrow was an object or not object this was basically done as the control to see whether objects, on the whole, are lateralized towards the left or the right hemisphere or not.
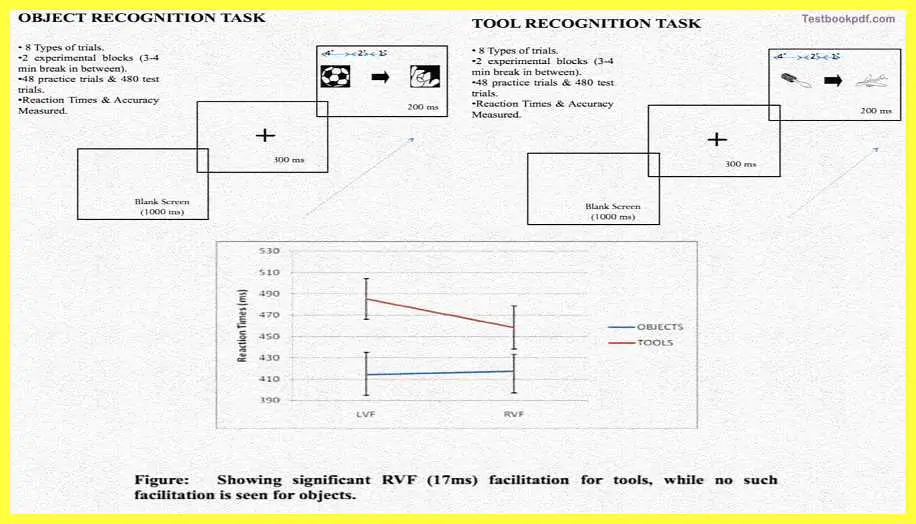
The second was the critical task the tool recognition task the participants had to tell whether the stimuli pointed towards by the arrow was a tool or not a tool. Very simple decision Yes No kinds of decisions.
What we found here was indeed recognized faster n a mood accurate fraction by in the right visual field which if u remember this process by the left, so in that sense it kind of you know conformed our hypothecs or for the fact left involved in the processing of tools.
Why should this happen to you?
Know two half of the brain differ with respect to these coactive functions this is something which is you know very dominative area in the field of cognitive psychology research something that keeps getting asked again and again there are certain theory’s about this but are the permanent theory.
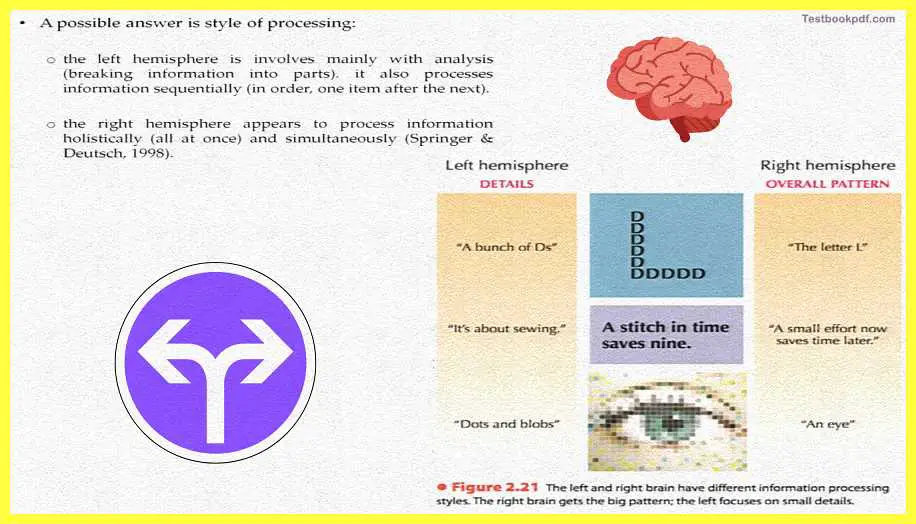
Basically, it talks about the style of processing so particular cognitive function or particular stimuli involve a particular kind of style of processing, and what we can say is that one hemisphere involve n one kind of processing while the other hemisphere involves in another kind of processing and it is with respect in the different style of processing that basically makes one hemisphere at dept at with processing a particular.
For example, the left hemisphere so involved in the main analysis and breaking down of u know larger sunk system into much smaller parts and it is also involved in processing information rather than sequence so all those steamily that need to be processed in sequence or that need to be broken down in more u know smaller components will evenly be processed better by the left hemisphere and all those stimuli that need to be processed holistically will then better be processed by the right this is one of the common theory that exists let us see
For example here if you see that there is an L is formed by a bunch of bees look at the same kind of simile the left hemispheres because it starts breaking it down into components will tell you that there is a bunch of bees in the right hemisphere on the other hand which has to look at the particular stimuli holistically will tell that it is just the later L. now you are seeing that is one stimulus that is being looked at differently by the two hemispheres depending on the style of processing that each of these hemispheres brings in.
This is pretty much what one of the basic explanations of hemispheric specializations, is put forward. Obviously, there are other theories as well but this is something that is commonly put forward.
Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex
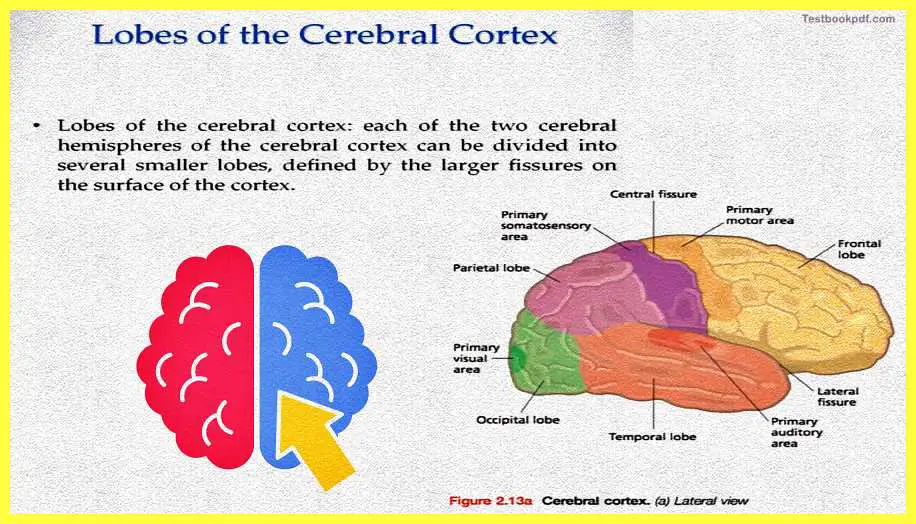
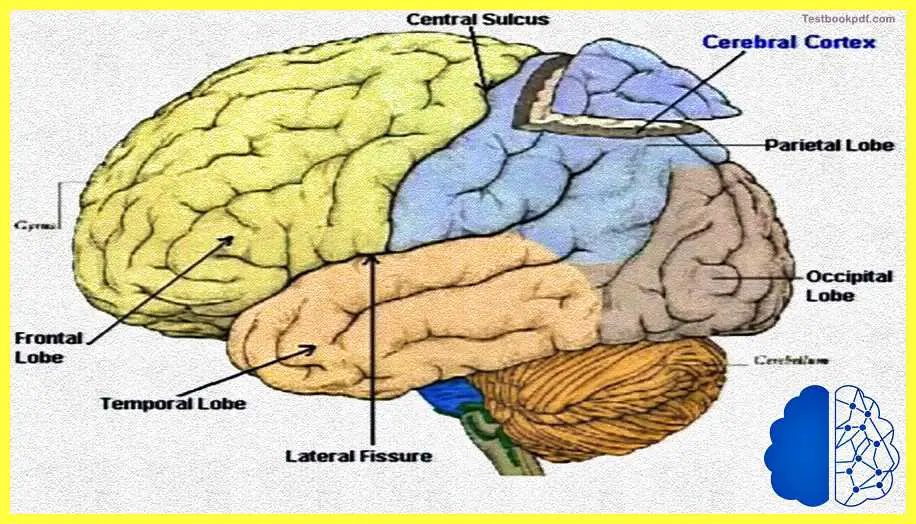
Now let us move towards the lobes of the cerebral cortex we talked about the frontal, the temporal, the parietal, and the occipital lobes, let us talk about these lobes in a bit more detail. Now, these lobes are the cerebral cortex basically can be divided into several smaller lobes, which are the lobes we actually talked about.
Now let us look at this figure you can see very clearly the parietal lobe, the frontal lobe, the occipital, and the temporal lobes. And you can also see that there are these areas the somatic sensory area. The primary motor area and the visual area which is actually lying in each of these lobes.
Frontal Lobes
Now let us talk about what the frontal lobes do. The frontal lobes basically are associated with higher mental abilities and they play a role in your senses of self say for example that idea I am somebody and these are my characteristics this is my behavior this is how I decide, this is my style of thinking all of this basically is and the sense of memory and that because memory provides you the sense of continuity that I am this person five years ago and five years hence I will be the same person is basically done by the frontal lobes.
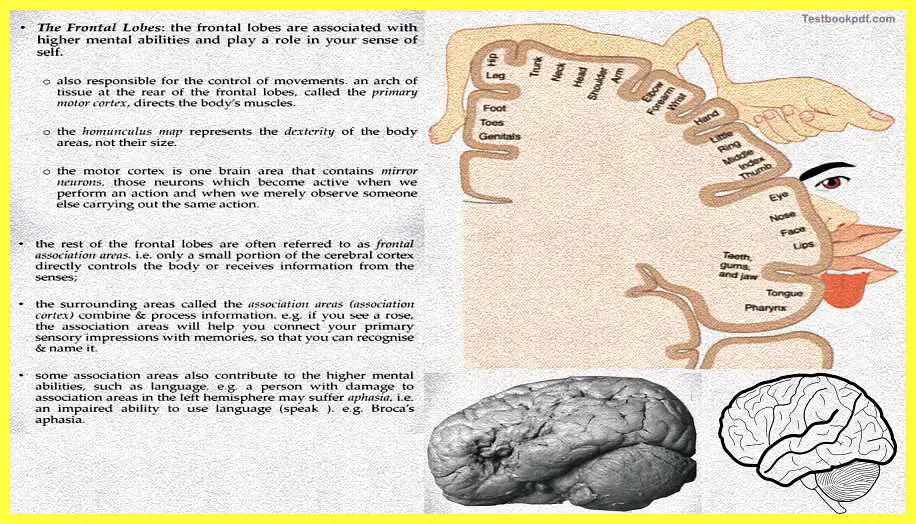
The frontal lobes are also important for movements and arch of tissue basically near the rear of the frontal lobes is called the primary motor cortex, you can see it right here is basically called the motor cortex, it is basically for controlling and directing various kinds of movement that the body makes there is this area in this primary somatic and this area is called a primary somatic cortex which is the homunculus map which represents the dexterity of the body with respect to different areas of the body.
I will show you the homunculus map in a while. The motor cortex again the part of the frontal lobes is the one area that also is supposed to contain things and a special set of neurons called the mirror neurons these are the neurons which are basically which become active whenever you are performing a particular action or even when you are seeing somebody perform a particular action so mirror neurons help you mimic and learn the same kind of action that you are observing at any point of time.
There are lots of theories that tell us those mirror neurons are very important for things like language and social behavior and so on. That is also one of the reasons you can say that the frontal lobes are involved in the kind of behavior that I mentioned Here you can see the homunculus map you can see the amount of neural tissue that is allocated to the processing of different parts of the brain is shown here you can see there is a large amount of neural tissue allocated at the face where there is relatively less amount of neural tissue allotted to, for example, the trunk, the neck, the head, etc.
The rest of the frontal lobes are basically referred to as the frontal associational areas that are only a small portion of the cerebral cortex which is directly controlling the body or receives information from the senses. The surrounding areas are called association areas which combine process information.
For example, if you see a rose the association areas will help you connect your primary sensory impressions with the memories you would have of the rose you will get those sensory impressions about the touch the smell, and the color of the rose, but the association areas will actually help you integrate your experience of the rose with an experience that you might have had earlier. You would come across a rose the first time, the second or tenth time every time you see the see he rose you actually get connected to whatever your previous experience was.
So some association areas also contribute to the higher mental processes abilities like languages, for example, if you want to write poetry if you want to describe something verbally those kinds of processes are also sometimes done by these different association areas. One example could be, that damage to the association areas on the left hemisphere may lead to a particular kind of disorder called aphasia, which is basically an impaired ability to speak the language. One of the kinds of aphasia is called Broca’s aphasia wherein the person actually cannot produce normal speech. The speech will be very jittery it will have ungrammatical sequences and the like.
Broca’s area
Here you can see the sample of somebody’s brain wherein there is this damage on the frontal part of the brain which is basically Broca’s area. Damage to this part actually leads to what I was talking about Broca’s aphasia
Phineas Gage and The Iron Rode
Now the very front of the frontal association region is the most anterior region called the prefrontal area of the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is related to more complex behavior like thinking, personality somebody being more sociable less sociable, irritable, or say for example civil behavior those kinds of things. If some of you were students of psychology you would remember a patient named Phineas Gage.

Phineas Gage was basically a railroad worker and in one of these accidents, he had an iron rod actually passing towards the front portion of his skull. After this accident happened the personality of everything remained rather the same but the personality of Phineas Gage changed considerably he began abusing people, speaking of profanities and he became less and less a civil person. So that is how you can actually link social behavior to the frontal lobes.
Coming to the parietal lobes, the parietal lobes register all these bodily sensations that are received from the sensory areas of the body, touch, temperature, pressure other somatic sensations basically flow into this area called the primary somatosensory area, which is there in the parietal lobes. We also notice the map of homunculus map that the map of bodily sensations is distorted, lips are larger in the drawing because of their higher sensitivity hands and fingers also occupy a large space because of their various functions. Here you can see that.

The Temporal Lobes
Coming to the temporal lobes, the temporal lobes are basically located on each side of the brain right above your ear. The auditory information projects directly to the primary auditory area which is there in the temporal lobe, making it the main sight where hearing is first registered. An association area in the temporal lobe is called the Wernicke’s area which is on the temporal lobe and is basically acting as the language site. This is the area that basically helps you comprehend whatever language you are hearing. Damage to this kind of area the Wernicke’s area basically leads to receptive aphasia which is a way to say that you will not be able to understand any language.
Wernicke’s Aphasia
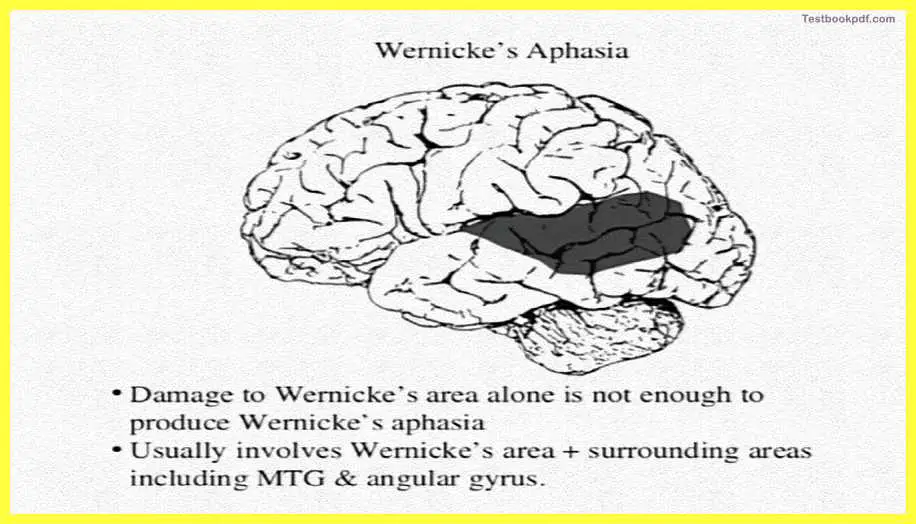
Here you can see the areas damaged which leads to Wernicke’s aphasia or receptive aphasia.
The Occipital Lobes
Coming to the occipital lobes, are at the back of the brain and are concerned with vision. How the visual areas represent vision is one of the questions that are asked much in cognitive psychology. So images basically are trapped from the retina to the cortex, but the map is rather stretched and greatly distorted because you will have to convert the dimensionality as well. The visual information areas are basically created complex patterns of activity of neurons and do not really send you a television-like image but rather a two-dimensional distorted kind of image.
Mindblindness
An interesting result of injury to the visual cortex or occipital lobes leads to something called visual agnosia, which is the ability to identify then seen objects. This is also referred to sometimes as mindblindness, for example, if you show Alice who is an agnosia patient an object you show a candle she can see it she will describe it as a long and narrow object, but she will not remember the name of the object. Because the information link between the occipital lobe to the higher associational area is somehow damaged.
In short, Alice will be able to see the colors eye shape, etc, but will not be able to form associations of these visual percepts to the memory and other higher centers of knowledge.
Are agnosia limited to objects only?
No agnosia can also happen to faces. for example, there is a variety of agnosia called facial agnosia, which is people’s ability to perceive familiar faces.
Facial Agnosia
say for example somebody who has an injury in the occipital area the area which is responsible for the perception of faces might suffer something called facial agnosia wherein the patient will not be able o recognize the faces that he had otherwise known, see one of these patients will not be able to recognize the face of her husband or mother when they visited her in hospital. She is not been able to identify the picture of her children, however as soon as they visited speaking she could recognize each of them because the auditory link was still intact.

So these areas devoted to recognizing faces lie in the association areas on the underside of the occipital lobes and they seemed to have no other function other than associating this visual input to other higher areas.
At the End
To sum up, in this article we talked about the structural and functional organizations of the cerebral cortex we talked about hemispheric specialization and we also talked about the structural and functional details of the other areas of the cerebral cortex which are the cortical lobes. Thank you.
Read also:
Basic Concepts in Cognitive Neuroscience ( Pdf Download )
Approaches Towards Cognitive Psychology
Click here for Complete Psychology Teaching Study Material in Hindi – Lets Learn Squad