Basics of Research Methodology Psychology Pdf Free Download
Today in this article we will talk about the Basics of Research Methodology Psychology Pdf Free Download and also give an overview of theory building, hypothesis testing, different kinds of research, and experimental research design. We will also learn how to examine our research findings and their validity.
What do psychologists do?
Psychologists generally are concerned with a variety of behavior both in humans and animals. They sometimes concede with problems relating to cognitive ability such as learning memory intelligence they are also sometimes concerned with dealing with psychological disorders what are the causes of how people suffering from those disorders can be helped also psychologies are constantly called upon to tackle issues related to education teaching instruction and so on.

Psychologists in reason in more reasonable times I have been finding use in developing driver safety manuals in deciding there optimal conditions for driving say for example for roads or train driving or even training of pilots also psychology have been involved with judging with scenario while criminal proceedings are going in course of justice.
How do psychologists actually deal with this?
What are the skills they use?
What are the methods they use?
Actually, these really are helpful for them in solving all of these kinds of concerns so let us talk a bit about the kind of research you do and the kind of research methods that actually the psychologists use.
Basic Kinds of Research

Primarily there are two kinds of research methods first is basic research, basic research is one that actually seeks to answer fundamental questions about human behavior, so something very specific something very simple says for example how do humans seek to color your something as basic as that or say for example how do humans distinguish between two kinds of shapes and those kinds of this thing another variety of research is applied research which basically investigates the issues that have direct implications in everyday life and it actually borrows from the findings from basic research from whatever the theory says and tries inputs it to use in solving everyday problems like the once we were just talking about, so that is basic research informs applied research and progress in any science actually happens only when both kinds of research are conducted so for our proposes we mostly be talking about concepts in basic research.
But we will also at some point about how these ideas from basic research can be carried forward to areas where they can be actually applied now what are the ground rules when psychologists actually take to research what are the first things that the straightness which psychologist make should be completely empirical they should be based on systematic collection of data and systematic analysis of data another characteristic.

What the psychologist aspires to is that the procedures use are completely objective and they are not really affected by the personal persistent are emotions of the person or the scientist conducting their research finally the data in the methods of collecting the data are described in detail and they are but in the public domain so that others may draw up on their own conclusion or even replicate the reported experiments And this kind of creative atmosphere of transparency in research and also sets out the data in the public so that everybody can derive their own kind of conclusions from the data that might available.
How does the psychologist organize the research findings?
So, wherever research findings are collected they need to be organized and transformed so that they can become part of common knowledge whatever research findings are there some kind of principles are generated principles need to be so general so that they can apply to all situations in a given domain of inquiry such generated principles are generally known as laws now this could be something conman to others empirical sizes as well say for example the loss of gravity on the law of action and reaction and those kinds of laws.
Organizing Knowledge
On the other hand, is an integrated set of principles that explains and predicts meaning but not all ossify relationships within a given domain of inquiry so for example if you are talking about a particular kind of behavior and you have certain principles to talk about one other thing to do is that to integrate all those principles in a kind of theoretical framework this theoretical framework should I really describe the phenomena in question exhaustively though it might sometimes not be able to explain all the possible relationship are all the possible phenomena within that head it should do you no rather good job of this stricken whatever goes on with respect to particular phenomena.

How does mean determine a good theory?
If you remember if talked about this any one of the earlier classes earliest go with this in a bit of high but let me remind you of what we talked about when you have to really evaluate a good theory one of the first things is that the theory should be about many different outcomes the theory be bored enough encamps many different outcomes related to particular phenomena at the same time the theory should be passive that it is it should have the simplest possible explanations about particular phenomena also a theory should fall.
For example, a theory that is not falls is able is not really testable and in the sense, if you remember what the purpose said they are not good theories finally theory should provide us a good idea so feature research say for example if you are conducting research on a particular topic it is hard to imagine that you will have answered all of the questions that where raise about that particular topic you want to leave some questions open or say for example they will certainly be some questions which you have not converted in your research.
This can be taken up by people in the further, who might be looking at your research and taking up those questions for in query existing theories that is why are modified on the base of collected data and the new modified theory then makes new perditions which are again testable so this is some kind of a cyclical arrangement which basically drives the research if you remember this kind of set up is referred to as the hypothetical deductive model which we have talked about in the past.
What are the main steps of starting to Conduct Research?
The first of the steps are basically two make rather let us say specific and restricted hypotheses what is a hypothesis is basically is a very specific falsifiable prediction about the relationship between two or more variables whether sleeping 6 hours a day has anything to do with your memory you will have to actually give a very n testable predicting that okay if one sleeps for x amount of hours the memory improvement is by a number by and then you should go you should be able to go out and test this relationship this is a specific hypothesis should be generally.

When you are talking about hypothesis, we are actually talking about the relationship between 1 or 2 variables now what is minimal, minimal basically is any other action we would that can assume different values amount different situations for example then let us say I am talking about as example I just gave sleeping now sleeping actually for a particular amount of time can take different values you can sleep for 2 hours 4 hours 6 hours you can have a night of disturbed sleep.
You can have a completely unreserved sleep and those kinds of things so sleeping in the framework of a particular study can be a variable one would like to study and what is the amount of sleeping actually this is one example of a way doing now one of the main problems when we which comes when you are actually talking about variables is that there are two kinds of variables probably first is conceptual variables, variables which basically stand from abstract ideas.
For example, if I talk about if I want to talk about the guild and those kinds of things these basically form the basis of research which is going to an idea is if you want to talk about kindness or guild those kinds of things as physiologically variables you would want to able to quantify them so that they can be actually made it so just now I said sleep can be measured into 4-6 hours that is the way I am quantifying sleep so for example kindness.
There should be a way for me to able to quantify kinds I should have the test or have a measure which can actually help me test the amount of kindness inserting so that part basically the conversion from a conception variable to something that can be quantified that quantified variable is called the measured variable, now how do you convert to take the conceptual variable and transform into a measured variable this process of converting a conception variable to a measured variable is called operational definition.
So, in the operational definition is per size statement of how a particular conception variable has been turned into a measured variable let me take n example here, say for example somebody says to you that. That physiotherapy reduces anxiety.
How do you quantify physiotherapy?
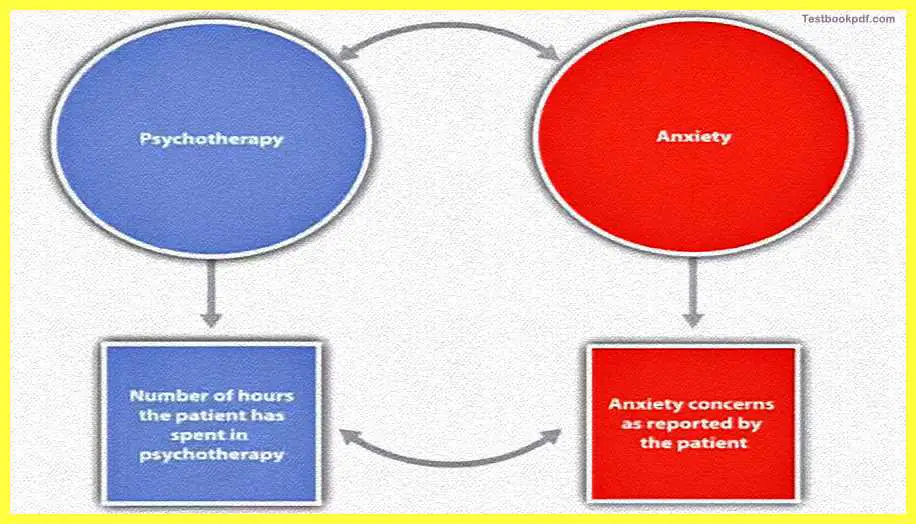
Physiotherapy is a rather brought drop it so what you can do is you can take an example saying a number of hours the patient has gone in physiotherapy actually reduces the anxiety concerns as reported by the patient so in that sense what you have done is actually convert it both of these conception variables, in physiotherapy and anxiety into measure those.
Now there could be other ways and there are some, some of the examples are required in which you can actually see that you converting these conception variables into measure variables see for example if you want to measure aggregations so one other thing could be said.

For example, you say a number of this second number of seconds taken by a person to start honking the car zone when he is stuck in about regular traffic jam or say for example if you want to measure depression.
You want to have a matrix for example – the number of negative words a question uses while writing a creative story so these are the ways in which you can actually now start to tangibly talk about these varies and that is one of the more basic things which drives any research enterprise.

Now there also different kinds of different types of research that can be done other than basic in applied research both of those kinds of research can actually be done through a variety of designs let us talk about what is the research designers, now a research design is basically a very specific method that research is used to collect analyze and interpret data’s you could have a question and then you can actually ask just which kind of research design I am going to use to answer this question.
Now there are three types of research design mainly first is descriptive research design which is intended to provide you a snapshot of the current state for example if you want just to check how many let us say how many people like the color red are living in your location so you can just go ask them that okay whether like the color red or not and then you can actually have a distribution that okay these many people like red and while others like some other colors the correlation research design.
Only the other hand is intended to discover the relationship between two or more variables it is basically used to allow for a prediction of the future say for example if you want to know the amount of humidity and then violence can be linked to the amount of rainfall that will be experienced later, so you can measure them also humidity and then you can then measure the amounts of rainfall that have to happen in try and find the correlation between that.
It is another second rather mathematical method another kind of research design is the experimental research type which is what we are actually concerned with when we are talking about permitting your physiology now in the experiment will research design one first needs to create an initial equivalent so for example whichever variable you really want to talk about and whichever groups you really want to look in with respect to the variable you would like to create an initial equivalence.
And then from there when you think all factors that are considered equal then you try and manipulate one of the variables which we regarded as an independent variable and then you actually measured the effect of this manipulation of the independent variable on another variable which is your dependent variable I will talk about this concept in more detail in this while.
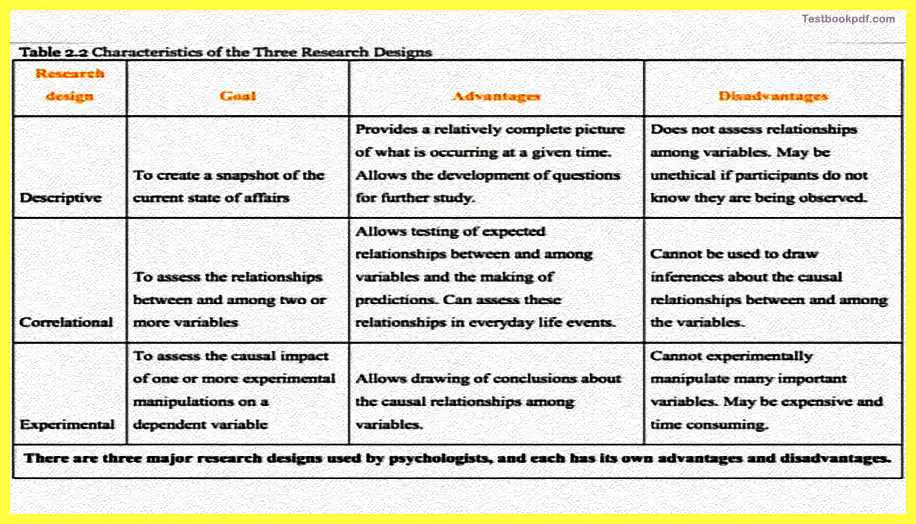
Now, this is basically a snapshot of how these different kinds of research designs are and what the advantages and disadvantages let us talk about them assuming it.
Descriptive research basically can be conducted in three ways you could either have studies varying your actually taking signal cases and describing them in detail what the behavioral patterns say for example of a person who is suffering from schemes of or let us say depress this order something like that, another way of doing descriptive research is conducting service you could have a question here which has let say 20 or 40 questions and those question basically tell you something about the population.

You can actually take these questions to the entire population or to a sample from the population and in that sense, you actually get an idea about whatever variables you are looking up another kind of descriptive research naturalistic observation, so for example if you want to see the variables in the plane in real settings so if you want to say want to check people say helping behavior while they are improving, so you want to relief go and observe.
Multiple groups and see how a particular scenario helping really takes the course and then this side at whether people help because of x or y variables.

Correlational research basically inverses the measurement of two or more variables as I already said and in the assessment of the relationship among these variables so, for example, height and weight may be systematically now people who are taller generally are considered to be heavier, those things like this one of these variables which you looking which will be looking for in the correlational design becomes predictor variable the other one becomes you are outcome variable.
What do you want to do?
Test the effects of the predictor variable on the outcome variable now there could be a variety of relationships.
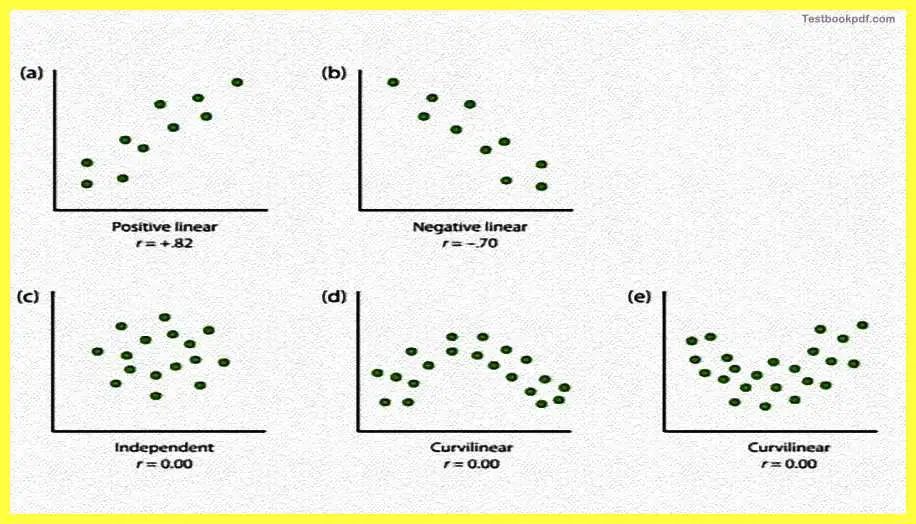
Among these variables, okay and those relationships are depicted in this figure here so you could have a positive linear relationship and negative linear relationship of those variables could be independent of each other, also you can see or they could be curving linear kind of relationship.
Now the most common statistical measure of the strength of linear relationships is the Pearson and Pearson’s correlation coefficient which is symbolized by the letter r. You might have seen this somewhere in papers or in particular books which you read. Now basically the directional of the linear relationship is indicated by the sign of the correlation coefficient that is r, so if r is + is there is a +sign then it is a positive linear relationship if it is a negative sign it is a negative linear relationship.
The magnitude or say for example numbers such as r is 0.5 4 or r is 0.79 it tells you how strong that relationship is, not about the direction but about the strength of the relationship. So if some, so if you want to measure the correlation between two variables and r coefficient comes up to be +0.80 you are actually talking about a very strong positive linear relationship. On the other hand, if the value is let us say, -r -.20 then you are actually if you going very weak but negative relationship.

Now the strength of this linear relationship is indexed basically by the distance of, as I already said distance of the coefficient from 0. Now because of the Pearson correlation coefficient, this r only measures linear relationships whenever you have a curvilinear relationship between two variables you will find that the value of r is 0.
It is also possible to study the relationships of more than two variables, we have been talking in our examples about generally two variables but it is also possible to test the relationship among more than two variables during a correlation coefficient sign, that kind of design is called a multiple regression set when it a statistical technique based on correlation coefficients among variables is used to allow predicting of a single outcome variable on the basis of a variety of other predictive variables. Let us take an example of that.
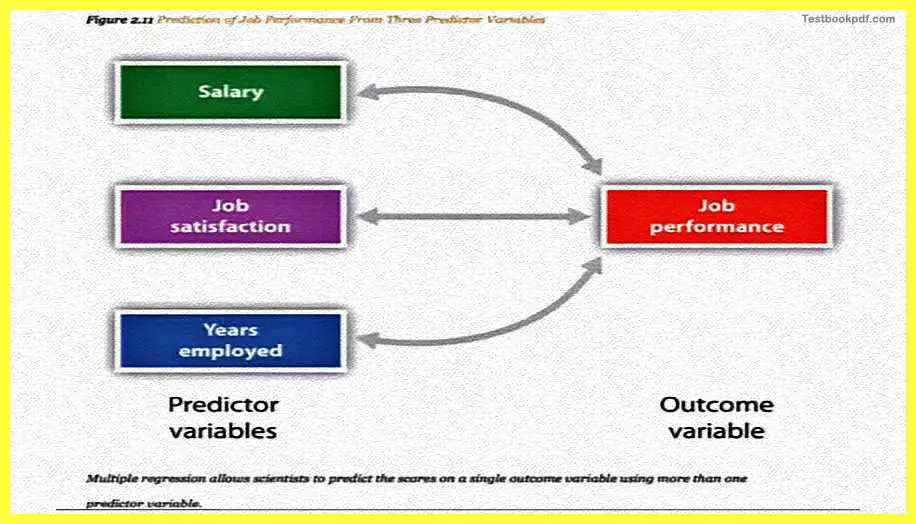
Say for example if you want to predict someone’s job performance you can actually talk about more than two variables you can talk about salary how the salary fixed their performance, how job satisfaction fixes job performance, or also the number of years that a person has been employed him. So can actually on the basis of regression coefficient tell how much a particular variable impacts the main outcome variable that is job performance.
Now there are certain, there are certain disadvantages to correlation research one of the disadvantages is that correlation research designs cannot be used to draw conclusions about the causal relationship you cannot really say confidentially that there is a causal relationship between the two variables which we were studying on the basis of a correlation design.
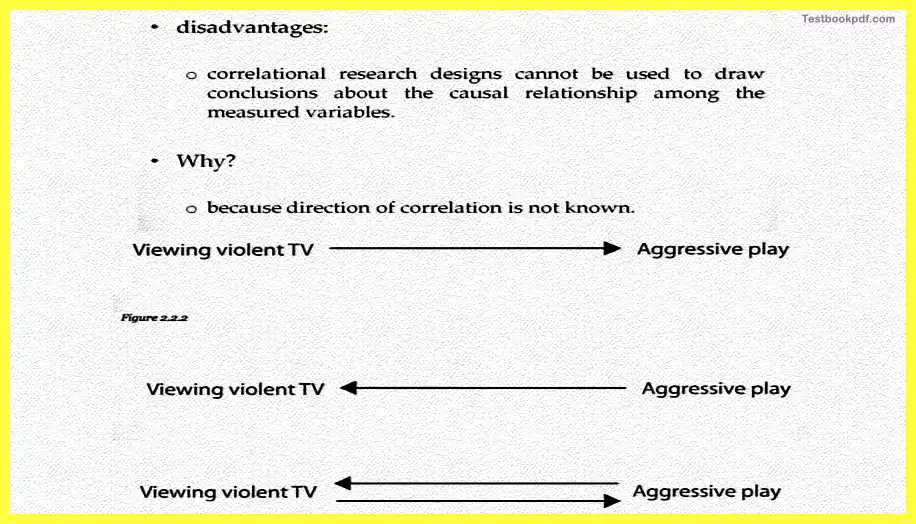
One of the reasons is that direction of correlation is not really known during this kind of method. So you might basically have let us say an example that if you want to study whether violent watching violent TV leads to aggressive play you will never know actually whether v viewing violent TV is leading to aggressive play or aggressive play is actually leading to more violent watching violent TV or say for example there is a bi-directional relationship. This kind of information is not given to us by the co-relational research designs.
See for example in some cases it could also be, that there could be a third common causal variable that is actually affecting both viewing violent TV and aggression.
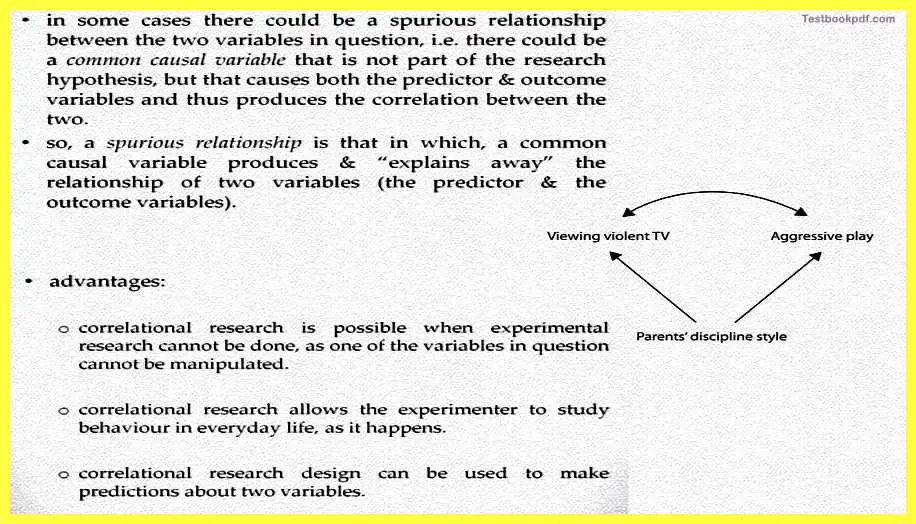
You could actually have some like this. That parent’s discipline style kind of effects the children in such a way that they, that there they view violent television and they also engage in aggressive kinds of play. So that kind of resolution is not there.
But there said an advantage also to correlation research design is it is generally possible when experimental research cannot be done. Say for example, if you cannot actually go out and manipulate the variables then it is one of the good ways to actually conduct research. Also, correlation research allows the experimenter to study behavior in everyday life you can actually just go take some measurements you do not really need to get inside that behavior and manipulated Also correlation research design can be used to make predictions about two variables.
Experimental Research Design
Now coming to experimental research design, let us talk about a scenario when even actually control variables another basis of that control in manipulation actually tells something about what is casually related to what, so as I mentioned earlier we are talking about two kinds of variables here, we are talking about an independent variable that is one which can be manipulated and we are talking about a dependent variable.
We will get manipulated or say for example on which we are going to measure the effects of the manipulation we did on the independent variable. Now we actually in an experimental research design we actually have these two kinds of variables and we generally create a testable hypothesis about how these two variables will be related.
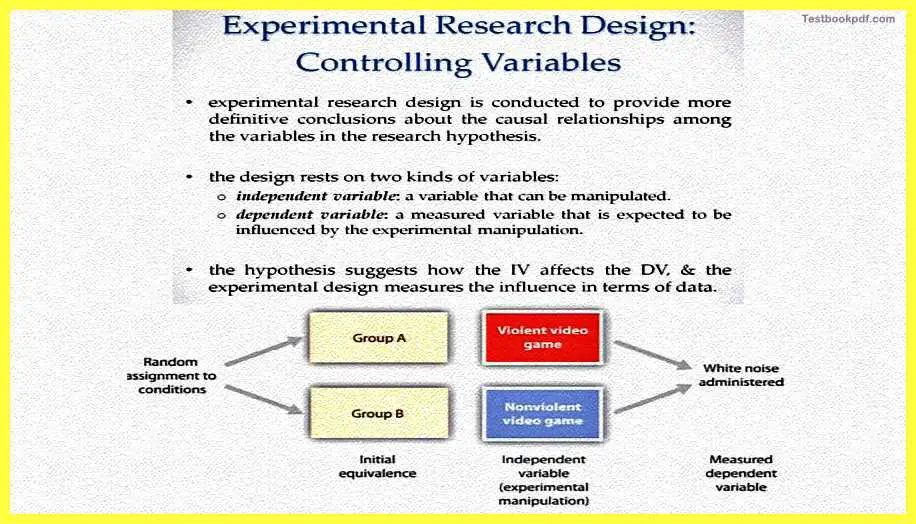
So hypothesis basically then suggests how the IV suppose to affect the DV which is how the independent variable is going to affect the dependent variable. And the experimental design is such that it measures the influence in terms of quantifiable data.
Say, for example, you want to really check whether viewing violence leads to aggressive behavior taking the same examples.
for example, what you will do is then you will actually have two groups I will say group A and group B you will create some kind of initial equivalence that they could be matched in A matched in other variables like pertaining style matched in the exploring to kind of TV they have matched in the general education of their parents social, now they could be many things you try and said how that okay, these are the parameters on which I will create kind of equivalence among these groups, then what you can do is then you actually give them a particular kind of treatment wherein you are manipulating the experimental variable or manipulating the independent variable.
So one of these groups actually watches a violent video game another of these groups watches a non-violent video game what you have manipulated here is the presence or absence of violent or non-violent video games. Then you actually take them to a scenario where they are allowed to express their aggression. So for example, you administer can particular kind of white noise and you actually see how the children are going to react to it, whether they react aggressively or whether they react non-aggressively. That is your way of actually measuring what is the dependent variable, and what is the outcome of this experimental manipulation.
Now two major advantages of experimental design are first that it assures you that the independent variable actually occurs prior to the measured variable because you created a kind of an initial equivalence. Second, this creation of initial equivalence between the conditions tells you that this effect is not arising because of any other factors.
How is this done?
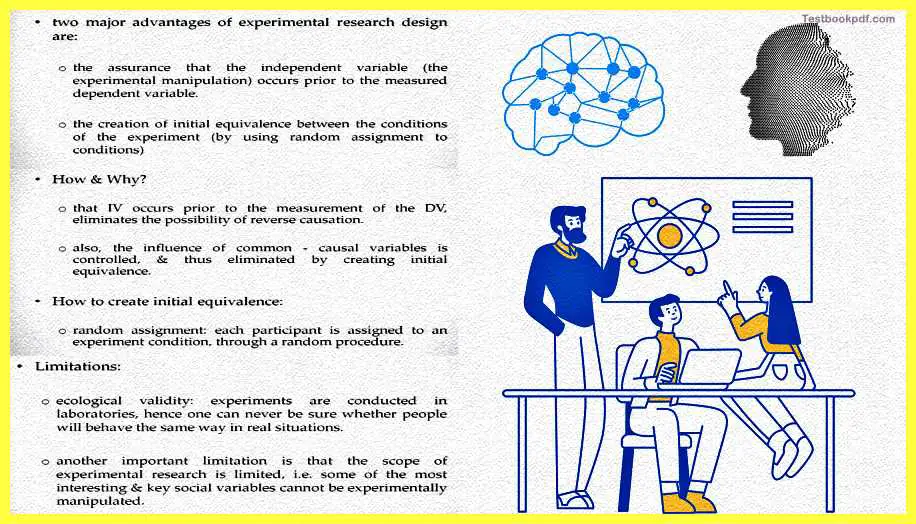
Because the IV generally occurs prior to the measurement of the DV that eliminates the possibility of reverse causation. Secondly, the influence of common casual variables is controlled by creating initial equivalence. How do you create initial equivalence generally random sampling or random assignment of participants to conditions are both ways in which you can actually create initial equivalence.
Now there are also limitations to the experimental research design as well, first is ecological validity now if you are actually getting into the play of the variables or actually controlling something this is not something you will actually do more often and not, so in one of the concerns that are always raised about experimental reset design is that they are these experiments are conducted under controlled laboratories settings and in that sense, they cannot be predictive of how the relationship between the wavelength spans out once the interplay is happening in the outside world whether there is not so much control.
Another important limitation is the scope of experimental research is rather limited. It is very difficult to know, to be able to manipulate all kinds of variables. So a lot of interesting key and social variables say, for example, the effects of religion or effects of rays extra are things that you cannot experimentally vary. You cannot have manipulated the rays versus religion of that person and then measure something.

So those are kinds of difficulties with experimental decision design.
Now I talk to you about the 3 kinds of research design and how research is typically conducted therein but say for example you have a set of finding and you want to be really sure of whether the findings are correct or not. So let us talk about ways where you can actually test it and be sure of it. Now there comes the idea of validity, so if you remember we talking about the experimental scenario, where somebody said that psychotherapy reduces anxiety.
What kind of psychotherapy we are talking about?
What form of anxiety we are talking about and does this really work?
Now the idea is asking this question will help you constrain your statements and in that sense, it will help you to get a very specific answer to your questions. Those kinds of answers are generally covered under validity, now, therefore, kinds of threats to validity. One of the threats is constructed validity, simply about whether the measured variable is actually measuring the conceptual variable. So see for example, if you remember one of the earlier examples that I told, whether the number of, sad words or depressive words a person used in a particular story really tells us about, whether the person is depressed or not. It might be that the person just likes that kind of thing and he is just using those words because let us say easily available words in the mind.
So does the number of these words really measure whether the person is depressed or not, that kind of question is asked when you are talking about construct validity. Statistical conclusion validity is the concern about whether the correct statistics have been used, and whether the correct methods have been used to actually defuse any kind of conclusion from the collected and analyzed data. Internal validity is basically about that is it possible that some of the variables have not been controlled and those variables are actually causing these effects other than the independent variable.
So that is internal validity finally, there is also the concept of external validity whether the results observed in the particular experiment are subjected only to a limited set of conditions or in my lab only or whether the same kind of results will occur if they test it in their own lab let us say in this same city, same country or somewhere else. So that is also, so that is the concept of external validity.
Let us talk about this issue in a bit more detail, construct validity basically refers to the extent to which variables using research adequately access the conceptual variables that they would design to measure. Say for example if you are using a thermometer whether the thermometer is actually measuring temperature or not, is such a basic question. Now an important requirement for a variable to have construct validity is the reliability of whether the variable is consistently measured, and whether the measures change in a matter of hours.
If the measures do not measure the conception variables, they are designed to measure then they cannot draw incidences about the relationship of variables in the question. So in that construct validity is instead an important aspect. Statistical conclusion validity refers to the extent to which we can draw, we can be certain the researcher has drawn an accurate conclusion so the static significance of the research finding, whether two things are statistically different or statistically significantly different from each other or not. There are two possibilities of errors happening here.
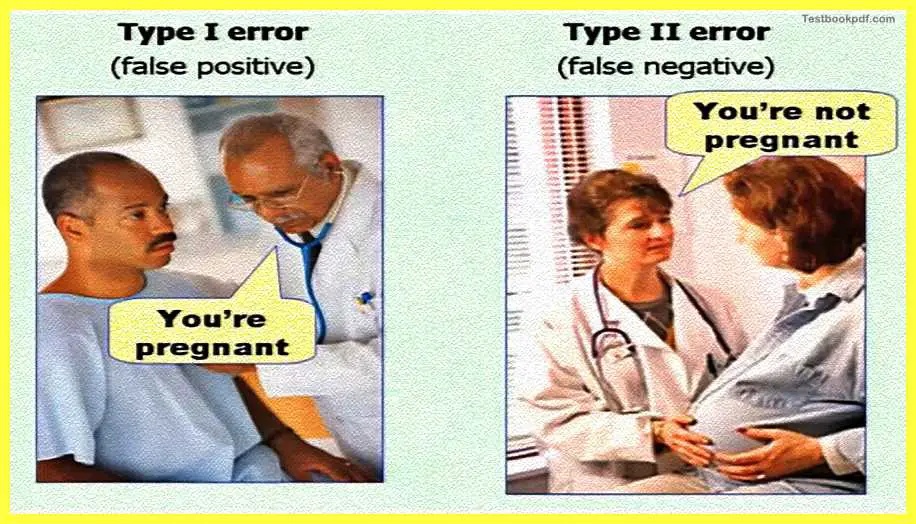
Say for example you can actually sometimes say that there is an effect if there is not, you can have something which is called a false positive, so figure on the left also you can say for the resembles figure on the left, also again you can some example find dismiss their effect when there is actually an effect that is called the false negative or the type two error. These are two common ways.
Now coming to internal validity, internal validity refers to an extent to which we can trust our conclusion and that had been drawn on the basis of our study of whether the same variable, is actually the variable that has caused the effect on the dependent variable. Internal validity basically has to do with experimental designs, generally, we try experimental designs such that we have control of all the possible variables that could have the effects and we make sure it is the only independent variable whose manipulation will lead to effects happening with the dependent variable.
Internal validity, therefore, is maximized if the confounding variables are minimized. No, we used the term confounding variables, what are confounding variables? A confounding variable is generally a variable that is not part of the research hypothesis or is mixed up or confounded with the independent variable, confounding makes it possible for us to be sure that it is the independent variable that has caused the effect on the dependent variable.
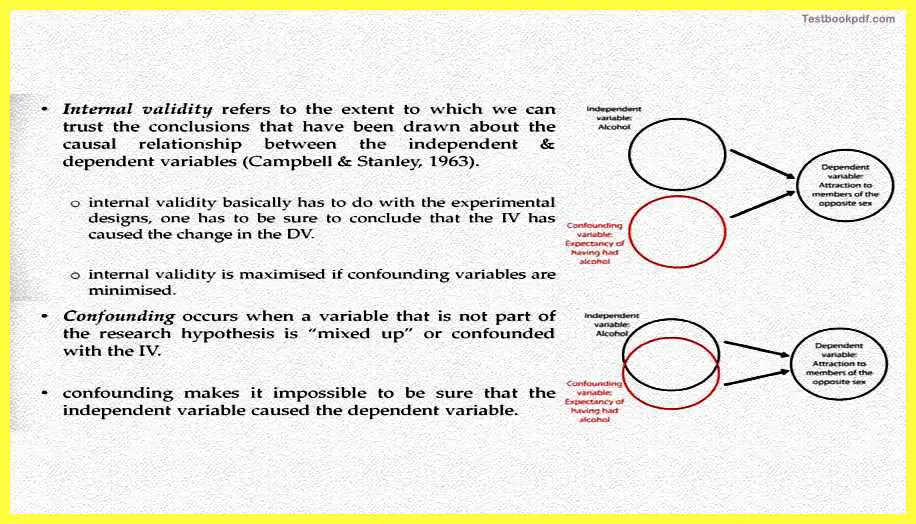
Let us take an example so there could be research where you want to test whether intake of alcohol increases a person’s attractiveness to the opposite sex. So the independent variable is alcohol and the confounding variable is expectancy attraction to the opposite sex. Now for example the group which is actually taken to be part of this experiment, if, for example, they know that they have taken alcohol and then the basis of that they start rating their attractiveness. The point is that they know sometimes thou might come up with incorrect conclusions.
You will never be sure whether the attractiveness towards the opposite sex, was only because of taking alcohol. To control these kinds of setups what we could do is, we can actually have a double mind setup where in we do not tell which members have been given alcohol, and which members have not been given alcohol, and then we measure the attractiveness of the opposite sex in both of these groups. Then what we can do is we can compare the attractiveness in both of these groups, the one who has taken alcohol and the other who has not taken alcohol.

In that sense that will give us the best estimate of whether taking alcohol had any effect on the attractiveness of the opposite sex. This is one of the ways. I remembered one of the studies in which I was involved, wherein I wanted to see whether the reaction times for happy faces or sad faces are equivalent or higher or lower something like that. You can see the know faces I have used here, basically, you can see the happy faces have a kind of confound. What is confounded? If you think for yourself and really look at these faces more, accurately you will find, that the happy faces both have teeth shown, while the sad faces do not.
In that sense whatever the result I would have drawn from this, might be because of the fact that teeth are been invisible so what I try to do is I try to change the confirm what I have done it was I tried to form pair the idea wearing the happy faces are compared with another kind of emotion say discussed.
Then wearing also the teeth alone now I can compare the reaction times to happy faces and discuss the faces it which show the teeth and in that sense, the comparison actually gives me only the effect of people’s perception of the facial expressions whether it happiness or sadness not because of teeth were visible one of them has set of stimulating more, easier to respond. These are one of the ways you could control internal value another way of controlling internal validity is to control experimental bias sometimes it could be that the experimental or the researcher himself or herself has a particular angle of an idea about what the result should be sometimes knowingly or unknowingly that could lead to the experimental affecting himself.
There is an interesting experiment we can talk about in this regard Rosenthal & Fode basically had two groups of students measure maze learning in rats so they basically give this bunch of rats and they were actually asked to measure how well or how poorly these rats would learn to navigate a certain kind of maze.
Now the point is one of these books wart will happen in this experiment one of these books were told that rats may be testing your highly intelligent the other groups they were told that rats were testing a highly and unintelligent now what happen was irrespective of what the rats would have ideally done or done in another scenario.
Both of these choices got results that are very consistent with the information they were given earlier so the first group actually found that, that the rats learned the mazes very well and the second would found that the rats could not learn the mazes as well and they kind of agreed with finalizing because they know that these rats are un-internal.
Now, this is one of the ways where the expectations of the next experimental kind of can get confounded with this how do you, control these experimental bias again as I said earlier the double-blind drug trials so something like in the formal industry people who are actually given medicinal dose they do not know and the maze of those drugs.

The doctors were giving these medicines also did not know which patients got the double bind got the +co and which patients got the medicine this is one of the ways you can actually control the experimental bias external validity coming to external validity basically refers to extend which the results of a research design can be generalized say for example whether the results can experiment conducted in my lab can be replicated in another lab or at another culture. You have the place something like that generalization basically refers to the degree to which the relationship among conceptual variables can be demonstrated in a wide variety of people and a wide variety of situations why do you need to talk about generalization so just to take a percent talk about this generalization basically is very important for any kind of research methods.
Because you do not conduct the research actually alone not only out of a sample of people you generally want to know about generally want to diffuse impedances about the large, larger number of population on the basics of research you do induce so all sample of people so the idea is that you research should actually be generalizable it should have in the result that it can be generalized for the large group of people.
Only then your research will have any value or any replicate value so toward extent let us say a particular result will replicate about people from different countries you can have an example here they were an experiment in which people wanted to easy that what kind of video game viewed can lead to what kind of behavior. So the same study was repeatedly done induced and it was found that more aggressive behavior also observed in people who washed violently video games and less aggressive people who are less aggressive behavior was also induced in people who watch less who played less violent videos.
On the point is we really want to test this in India or in Japan or in China it would actually want to do this same study in these places and see whether this kind of relationship will hold or not now just to give you a small tip is that none of these research design so no research design can possibly be proven to generalize in all situations.
You have to make that inference on the basis of how well you control all the other variables and all the other important factors at this time so one basically assumes so on the basis of these kinds of measures that while conducting experiments the results obtained will generalize the two other populations.
At the End

As to sum up we can know that advances in science occur through the accumulation of the knowledge that comes from many different tests of the same theory, okay so you can have a correlation design you can have a variety of research designs and you can ask this same question now many research designs there are different kinds of participants. And another most important factor is the operation of how you operationalization in the independent and dependent variables scientist to actually ensure that the research has been unavailing or to actual take stop of what kind of research exists in the particular field take two something called meta-analysis, meta-analysis basically is a statistical technique that uses the results of all the existing studies or many existing studies in a particular field.
To integrate them and to draw a conclusion on the overall topic Meta-analysis is actually or rather a powerful and very useful way of summarizing the entire research literature related to specific terms it will provide you a relatively objective way of reviewing research findings because you actually compare these different research findings. And particular scenario also specifies the inclusion criteria so exactly what kind of research that is over what kind of participants in what kind of conditions you are actually comparing that will be giving you a very good hold on what can be really induced on this also meta-analysis is systematically researched for all the studies that pretend particular illusion criteria.
for example, you want to study to tell you about intelligence and memory announce people of age characteristics 8 to 10 and 12 so you can actually prefer all the studies which have use and study the same questions it also provides you in the objective measurement of the strength of the observation. If we actually find that particular kind of result happens in only 20% of results studies and 40% of studies say something else then you can actually compare the strength of the mind you can actually take up all that whether it was a strong conclusion to take or not.
So, to sum up, in today‘s article we talked about the variety of research methods and we talked about theories and problems we said we talked about kinds of research designs we also talked about what kind of variables we ask questions about and we talked about statistics and validity thank you.
Read also:
Basic Concepts in Cognitive Neuroscience ( Pdf Download )
The Cerebral Cortex Psychology Theory, Images, Pdf Download
Click here for Complete Psychology Teaching Study Material in Hindi – Lets Learn Squad



